Institut Pierre Simon Laplace Studying the climate system as an integrated system - CMM
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
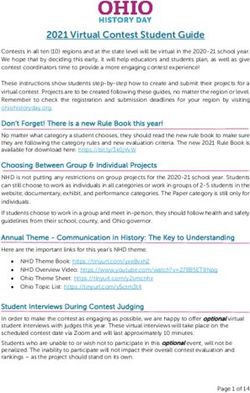
The IPSL Earth System Model
LMDZ
LMDZ ORCHIDEE
Continental surfaces
Atmospheric
Atmospheric physics
physics and
and
INCA/REPR0BUS dynamics Vegetation, Hydrology
dynamics
Atmospheric chemistry
Air quality
OASIS
Coupler
LIM
Sea Ice
PISCES
NEMO Marine biochemistry
Ocean Physics and Dynamics
Page 2CO2 and methane assessment
Flex: Growing plants observed IASI –NG: composition
Here: Merlin a methane project
through fluorescence (ESA) atmosphérique (gaz, aérosols)
(CNES/ DLR)
Involved (through its laboratories, but also in its coordinating role)
in a very wide range of space missions
Calipso : Cloud and aerosol
Feedbacks, (NASA/CNES)
EarthCARE (ESA)
…. and Megahtropics, Mescal,
SWOTCooperations with South-America
- 1991: Initiation of European Projects (4 projects, during 20 years
approximately, including the 2 Claris Project lead by Jean-Philippe
Boulanger) . South-American contribution: Mercosur Countries and
Peru.
- 1 January 2001: UMI-IFAECI (Unidad Mixta Internacional: Instituto
Franco-Argentino Sobre Estudios del Clima y sus Impactos)
- Large interdisciplinarity
Institut Pierre Simon Laplace Page 4 Page 4Climate change:
A new phase in a quickly evolving problem .
- We increasingly engage the future (« climate debt »)
- Going from alert to solutions requires an increased attention to
new issues: vulnerability of the « eco-socio-systems », complexity
and interdisciplinaritity of the choices
Institut Pierre Simon Laplace Page 5 Page 5CO2 emissions from the use of fossil
fuels: still increasing (International
Energy Agency).
Eath Summit 1992
International Energy AgencyWhat are the authorized emissions to stabilize
under a 2°C warming Required CO2 emissions
IPSL / IPCC 2013 (in Gt per year)
Targeted Earth Surface
IPCC
Temperature Changes
(in °C)
Scale of glacial
interglacial
climate changesFuture Climate Trajectories
Required CO2 emissions
IPSL / IPCC 2013 (in Gt per year)
IPCC
Avoid any delay
Methane , Pollution
Structural
actions
Transportation
networks
Urbanism
Negative emissions
CCS, BECCS,The view of a few years ago: sharing the current emisions
Here the emissions per person in tons of carbonClimate evolution: RCP 2.6 (above) Nasa GISS observations (below)
Impact of nation contributions
2015 2030
Impact of the emission reductions contributed by the different nations, as estimated
by the GICN during COP21Depuis 1970 : - production d’énergie pimaire x 2 - population mondiale x 2 - répartition par forme d’énergie inchangée
The adaptation of territories to global changes)
A necessary protection against climate risks ,
Based on a vision of future climate evolution
Requiring multidisciplinay science
and the closest interface with decision making
Institut Pierre Simon Laplace Page 16 Page 16The Acclimaterra project: an investigation about
Bordeaux and New-Aquitaine areas
Hervé Le Treut, Sorbonne University
Director of Institut Pierre Simon Laplace
ADAPTATION ISSUES
DIALOG WITH CITIZENS
WIDER CONTEXTThe muitidisciplinary approach of Regional Climate
Changes: AcclimaTerra Reports on the SouthWest of
France (Aquitaine and New-Aquitaine)
First one
published (Released 1st
in 2013 June 2018)
(Le Treut, 2013)
http://www.acclimaterra.fr/
Page 18Evolution of food requirements for the different
continents (FAO, cited by Benjamin Sultan IPSL/IRD)
Continent Increase factor from
2000 to 2050
Africa 5
Asia 2.5
Europe 1
Latin América 2
North América 1.5
Oceania 1.5Are the results of science really used by decision maker? 09/09/2019
Main issues
From global to local
Vulnerability: social
concerns, preservation
From past to present and future of the biodiversity,
(role of memory)
Key areas: mountains,
shorelines, humid zones
Resources: water, agriculture,
forestry, wine, energy, fishing Governance (role of law, of
activities public
debates)
Health and sanitary risksTemperature evolution in « New-Aquitaine » over the
last 57 years
+1,4 °C au cours de la période 1959-2016
Second rapport AcclimaTerra à Page 22Agricultural droughts over the same period
Évolution du pourcentage de la surface de la Nouvelle-Aquitaine où l’on a observé des conditions de
sécheresse agricole au cours de la période 1959-2016. L’hiver correspond à la couleur violette, le printemps
au mauve, l’été au jaune et l’automne au bleu. Le trait noir représente l’évolution de la moyenne par période
de 10ans. Source : Météo-France.
augmentation de l’étendue des sécheresses agricoles de 6 à 7 % depuis
1959
Second rapport AcclimaTerra à Page 23Looking at regional climate as a unique complex system
(from a study about the Bordeaux province in France)
Meteorological changes
Snow, Mountains
Moyenne annuelle des débits de Garonne et Dordogne
1000
moyenne Garonne
900
moyenne Dordogne
800
700
Air quality
Débits (m3/s)
600
500
400
300
200
1959 1969 1979 1989 1999 2009
Années
Biodiversity Health
Summertime rivers
, Hydrology Fishery
and sea
resources
Littoral areas, erosion
Nuclear plantThe cities at the interface between
adaptation and attenuation
A Heat wave in Bordeaux
27 August 2016The energy mix at the interface between adaptation and attenuation
In memory to : Michel CombarnousWe requires both fundamental and applied
research
- The limits of what is predictable or not are not well known
- We need to explore climate changes as the changes of
a complex system, which requires mutidisciplinary approaches
- A more comprehensisive approach of the link between
global and local perspectives. It is also a source of innovations in
many domains (« Big Data » in particular)
Institut Pierre Simon Laplace Page 27 Page 27The challenges of the future - Meeting simultaneously the needs of a limitation of greenhouse gases and those of adapting to a future warming that cannot be completely avoided - Develop a sufficient level of understanding in the population - Avoiding dangerous wrong solutions (« management of solar input ») Institut Pierre Simon Laplace Page 28 Page 28
Water availibity: A unique ressource although distributed in different areas: rivers, surface, deep storage
Solution space = confrontation with complexity
…. and innovation
Radiative forcing of atmospheric emissions, IPCC, 2013Captation/sequestration for C02: necessary but not yet at
the right scale (billions of tons)
1. capture by photosynthesis and strorage in deep
geological layers
2. surface storage through modified agricultural practices
INRA 4/1000 project
Page 31Project management A council of 21 scientists from physical to social scientific disciplines, Initiated and supported by the local government, but fully independant First step of the work based on careful assessment of existing science leading to two comprehensive reports (2013, 2018), published as books Active participation of about 400 senior scientists 20 cities visited, with a range of outreach activities targeting the elected representatives, companies, citizens, high school and university students A huge amount of information which is never accessed in a systemic way
AcclimaTerra Main Council •Hervé LE TREUT – Sorbonne Université – Président d’AcclimaTerra •Nathalie CAILL-MILLY – Ifremer – Laboratoire Environnement Ressources d’Arcachon •Bruno CASTELLE – EPOC – CNRS – Université de Bordeaux •Michel COMBARNOUS – Membre honoraire •Daniel COMPAGNON – Centre Emile Durkheim – CNRS – Cciences Po Bordeaux •Frank D’AMICO – UPPA •Julien DELLIER – GEOLAB •Alain DUPUY – Bordeaux INP •Henri ETCHEBER – Membre honoraire •Emmanuel GARNIER – CNRS •François GASTAL – INRA Lusignan •Antoine KREMER – INRA Bordeaux •Bernard LEGUBE – Professeur émérite de l’Université de Poitiers •Agnès MICHELOT – CEJEP •Virginie MIGEOT – INSERM-CIC
Sensitive areas, with different forms of risk:: the shorelines
Precipitation evolution is difficult to diagnose
Second rapport AcclimaTerra à Page 35Climate natural variability affects future changes Cassou, CNRS CERFACS
You can also read