REFLECT#01 IMPULSE by ENGIE REFRIGERATION - CO2 HIGH TEMPERATURE HEAT PUMPS
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
CO2 HIGH TEMPERATURE
HEAT PUMPS
SUSTAINABLE & EFFICIENT
THE REFRIGERATION MAGAZINE FROM
ENGIE REFRIGERATION GMBH
REFLECT
IMPULSE
#01
2018
by ENGIE REFRIGERATIONAn intelligent use of heat pumps makes it possible to raise the generation of cold and heat to new levels of efficiency for all kinds of applications. In June 2018, ENGIE Refrigeration added heat pumps with CO2 technology to the existing heat pumps in its portfolio. This natural refrigerant is powerful, especially climate-friendly and non-critical to use. CO2 HEAT PUMPS – POWERFUL AND CLIMATE-FRIENDLY PUMP IT UP! 2 REFlect | Issue 02/2018 3
Heat pumps are an especially intelligent and sustainable
way of generating heat out of energy from renewable
sources. These machines are equally suitable for all
kinds of commercial and industrial buildings and facilities,
including swimming pools, for example. And heat pumps
are more than just an energy-saving and environmentally
friendly way of heating. Intelligent concepts make it
possible to use just one system to provide heat in the
winter and cooling in the summer. In the same way, it is
possible to simultaneously generate heat and cold – for
example, in offices and food storage spaces.
Exploiting unused potential New: CO2 as a refrigerant High-temperature heat pumps like the Long-term trend towards natural refrigerants
The fundamental principle of heat Chillers from ENGIE Refrigeration are thermeco2 can handle both the heating In general, major changes are happening at the moment in the field of refrigerants: “Environmentally harmful HFC refrigerants are
pumps is to absorb heat at low tem- especially known as highly efficient process and the heating of drinking wa- being replaced by HFO refrigerants, and increasingly by natural refrigerants as well,” says Stiegelmeier. “In the long term, a trend
perature levels and dispense it as cooling generators. However, they are ter in full, so that no electrical additional towards natural refrigerants seems likely, due to the F-gas Regulation, which is currently leading to restrictions on volumes of halo-
useful heat at a higher temperature. also excellently suited as heat pumps, heating is required. CO2 stands out be- genated refrigerants.” Cold and heat pump technology is a key technology of the future. If we stop generating power from fossil fuels
Jörn Stiegelmeier, head of techno- and have already been successfully cause it is harmless to use (classified and instead generate it from renewable energy sources whose availability is permanently shifting, we will need storage facilities to
logy and development at ENGIE used for this purpose by various industrial as A1), cheap to procure, and, with a provide load balance. Thermal storage can provide this load balance. CO2 is a highly suitable refrigerant for efficient thermal energy
Refrigeration, explains the benefits of customers – often for combined heat- GWP of 1, has no harmful effects on the storage. In case of excess power in the grid, hot and/or cold thermal energy storage units can be charged with a CO2 heat pump and
the technology: “A heat pump uses ing and cooling. earth’s atmosphere (see Q&A). CO2 (in discharged again when power becomes scarce.
heat sources that are normally techni- subcritical mode) has become standard
cally not usable. For instance, a heat In June 2018, our portfolio was expan- for use in refrigeration – for instance,
pump can increase the temperature ded to include high-temperature heat in the cooling and storage of food. At F-gas Regulation
of geothermal energy from 10 °C to pumps and drying technology with CO2 higher temperatures (supercritical
40° C.” In addition to geothermal ener- technology. With the help of this natural mode), it is possible to implement
gy, it can utilise surface water and refrigerant – whose technical name is heat pump applications that are highly The F-gas Regulation published by the European
seasonal heat stores as heat sources. R-744 – it is possible to achieve effec- efficient in their respective temperature Parliament and European Council came into effect
But a heat pump only lives up to its tive temperatures of up to 110 °C. This ranges. Supercritical applications are on 1 January 2015. Since that date, refrigerant filling
full potential in terms of performance opens up applications in the fields of a relatively new field of application for capacities have been weighted according to their
and sustainability when it converts heating, heat provision in communal and CO2 as a refrigerant. “It can make a lot global warming potential. The F-gas Regulation is
waste heat from industrial production, industrial heating networks, and drying of sense to use CO2. What is important intended to reduce the volumes of fluorinated green-
exhaust air from air-conditioning sys- technology, for instance in automotive is the expertise to identify applications house gases (F-gases) put into circulation in the EU by
tems, or waste heat from chillers and paint shops. The device series is on the where CO2 is the perfect refrigerant, 79% from 2015 levels down to 35 million tons of CO2
then makes it available as heat output market under the name of “thermeco2”. and applications for which it is less suit- equivalent by 2030. This objective is to be achieved
at a higher temperature level. Because able,” says Stiegelmeier. “CO2 is pre- by three measures in particular:
it optimises such processes, using a Standard heat pumps are usually inade- destined for all applications that require
heat pump generates significant ener- quate for heating drinking water. When colder temperatures and a lot of heat
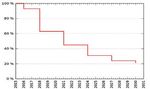
1. A step-by-step restriction of the F-gases available on the market; by 2030, they should be down
gy savings. drinking water is heated, heat carrier at the same time, such as an air-condi-
to 21 per cent of the amounts generated in the reference years of 2013 to 2015
temperatures of 60 to 70 °C need to tioned hotel with a swimming pool and
(phase-down scenario; see figure)
be achieved in order to kill off legionel- sauna, for example.
la. These high temperatures are usually
2. Prohibiting the sale of refrigerants with high GWP values
generated by means of an additional
electrical heating element. However, this
3. Extending existing regulations on leak tests, certification, disposal and labelling
is not very energy-efficient, as electric
power is used for the heating process.
4 REFlect | Issue 02/2018 5GWP – global warming potential of refrigerants What are the Why is CO2 non- What are the techni-
The GWP value (global warming potential) is a CO2 equivalent that determines the relative green- advantages of CO2 harmful as a refrig- cal challenges posed
house potential of a chemical compound. This measure describes the average warming effect on as a refrigerant? erant even though it by systems that use
the earth’s atmosphere over a specific period (usually 100 years). It thereby specifies how much a
defined mass of a specific greenhouse gas contributes towards global warming when compared to
is such a big problem CO2 as their refrige-
• Future-proof: a natural substance, so
the same mass of CO2. For example, the GWP for the refrigerant R-134a for a period of 100 years no usage prohibitions or restrictions as exhaust gas from rant?
is 1430. This means that one kilogramme of R-134a will contribute 1430 times as strongly to the are to be expected. combustion engines?
greenhouse effect within the first 100 years of being released as one kilogramme of CO2. • Very good availability • High efficiency during supercritical
• Climate neutral and environmentally operation in the interior heat
• CO2 refrigerant operates in a cycle
friendly exchanger
process and is not released or
• No additional contribution to the • Greater control required during
emitted as it would be during a
greenhouse effect (GWP = 1) supercritical operation
There are other commonly used natural refrigerants apart from CO2, for instance ammonia (NH3) and propane. However, due to the combustion process. It can only
• No contribution to the destruction of • For maximum efficiency, the required
dimensions of chillers and their correspondingly large refrigerant filling capacities, propane is a problematic and explosive substance escape in the form of a leak. Leaks of
the ozone layer temperature regime needs to match
when it comes to leaks and maintenance. It is suitable and manageable when used in chiller units containing less than one gram of a refrigerant with a GWP value of 1
• Non-toxic, non-flammable, thermally the way the CO2 heat pump is
refrigerant, such as those used in supermarkets. “Consequently we have been working with ammonia and CO2 for many years and are non-critical.
stable, suitable for materials operated.
developing chillers and heat pumps for these natural refrigerants,” says Stiegelmeier. • No environmentally harmful contribu-
• Safety group A1 • Pressure situation of 120 bar calls for
tion to the overall CO2 balance: all the
• Low running costs when compared suitable pipe dimensions, but is easily
CO2 involved existed beforehand; no
to other natural refrigerants manageable in technical terms. In
newly generated CO2 is released.
vehicle manufacturing, for example,
Eleven performance classes with CO2 • CO2 refrigerant is a by-product
much higher pressures of up to 2,000
The new range of CO2 heat pumps from generated by plants operated by the
bar are customary for common-rail
ENGIE Refrigeration comprises eleven chemical industry.
injection.
performance classes between 45 and
1,440 kilowatts. Currently machines in
the performance class of 500 to 1,000
kilowatts are the most popular. Models
are also available in a hygienic stain-
less steel design, making them ideal for
sensitive applications such as the food
industry.
Reference
AMONUM in container format Know-how in the team
Chillers with a natural refrigerant are not The experts at ENGIE Refrigeration are The thermeco2 machines add high-
new territory for ENGIE Refrigeration: currently examining whether the market temperature applications to the ENGIE CO2 heat pumps for SWR
the AMONUM series was launched in requires machines with an even higher Refrigeration portfolio: QUANTUM
2013. The AMONUM stands out be- performance. “Reasons of redundan- reaches approximately 55 °C; The buildings of the Südwestrundfunk (SWR) broadcaster in Baden-Baden
cause it has a compact design for a cy suggest that multiple powerful ma- SPECTRUM with screw technolo- require a lot of energy to run. Until 2012, SWR generated its own cold and
chiller and heat pump, and it has pro- chines are a more sensible choice than gy reaches approximately 60 °C; heat centrally with a water-cooled liquid cooler and large boilers. In order
ven itself. With a weatherproof housing, one extremely large heat pump,” says AMONUM with ammonia as a natural to improve the efficiency of the systems, the SWR technology department
the machine can be set up outdoors. As Stiegelmeier. “Market and customer refrigerant reaches approximately 60 decided to find a new, efficient and ecological solution to cover the basic
ammonia is classified as toxic, corrosive demands will determine the right path in °C; and thermeco2 with CO2 reaches heating load. Engineers achieved their aim with the help of a CO2 high-temper-
and hazardous to water, operating com- future.” approximately 110 °C. ature heat pump from the thermeco2 series, which became part of the ENGIE
panies face stricter demands when Refrigeration portfolio in mid-2018.
setting up and operating NH3 chillers The thermeco2 series machines that
and heat pumps than they do for CO2 have already shipped around the world The HHR 360 high-temperature heat pump combines the generation of heat and cold. For the SWR building, it generates thermal heat
chillers and heat pumps. That is why will be looked after by the international of 40/80 °C in parallel to the new large boilers and uses the waste heat directly from the network of chilled water for climate application
ENGIE Refrigeration offers an AMONUM ENGIE Refrigeration service network. to do so. In addition, the HHR 360 reduces waste heat losses from refrigeration and relieves the existing chillers and recoolers. SWR
container solution, which represents a “Our entire organisation, from sales and chose a heat pump with an eco-friendly refrigerant because its use will not be restricted in future, e.g. by the F-gas Regulation. In
separate and independent machine consultation to service, is adjusting to addition, the new heat pump lowers CO2 emissions when compared to a heating system based only on fossil fuels.
room. The operating company benefits the new portfolio,” says Jörn Stiegel-
by receiving a turn-key solution with the meier. “At ENGIE Refrigeration, we view By running the CO2 heat pump, SWR has lowered heating costs by a third. In addition to the annual heating capacity of the heat
relevant safety precautions outside its ourselves as a team that takes care of pump, the cooling capacity and avoided re-cooling work also flow into the efficiency analysis. Because of these positive results, SWR
in-plant production sites. all technologies and customers, using its ordered another HHR 520 thermeco2 high-temperature heat pump in September 2013 to supply a different part of the building with
extensive know-how.” heat and cold.
6 REFlect | Issue 02/2018 7IMPRINT PUBLISHER ENGIE Refrigeration GmbH Josephine-Hirner-Straße 1 & 3 D-88131 Lindau, Germany Phone: + 49 8382 706-1 Fax: + 49 8382 706-410 refrigeration@de.engie.com engie-refrigeration.de EDITORIAL RESPONSIBILITY Tatiana Köhler, Head of Marketing and Communications EDITORIAL DEPARTMENT Publik. Agentur für Kommunikation GmbH TEXT/EDITING AND DESIGN Tatiana Köhler, Katja Krimme and Jessica Ritzenhofen TITLE DESIGN Internship work from Mats Erdmann PICTURE CREDITS ENGIE Refrigeration GmbH (pp. 10, 11), tcharts ( pp. 6/7), Petmal (p. 9), robertsrob (p. 10), RomoloTavani (p. 11) October 2018 Optimal use of energies.
You can also read