THE MOLECULAR ORCHESTRA - AN INTERACTIVE INSTALLATION - Jill Scott
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
A F T E R T A S T E
THE MOLECULAR ORCHESTRA
A N I N T E R ACT I V E I N STA L L AT I O N
by JILL SCOTT
Molecules are like families in an orchestra; together they stimulate our senses (taste, smell, sight, hear-
ing). AFTERTASTE invites you to play with 24 interactive molecules in order to discover the complex bio-
logical interaction of the molecular families of the chicory root and to learn about the biodiverse potentials
of wild root crops. In Europe wild plants like chicory can be re-introduced as crops to enhance the levels of
biodiversity in the soil and in our food chain.
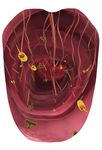
AFTERTASTE consists of a sound installation and of good bacteria in the colon and substitute sugar,
a model of the olfaction system, with video projec- Phenolics are known for their anti-toxic and anti-oc-
tion mapping on a large 3D sculpture of the human cident activities in the body. Nutrients and minerals
tongue. Through interaction the visitor can explore also have a great range of health benefits.
the health values of molecular compounds found in
wild vegetables roots and the increased health ben- Taste and smell combine to register flavor of food in
efits of eating them. Here the compounds of interest the brain. This is often called an aftertaste. Hence the
are based on the molecules of Terpenes, Phenolics, title “Aftertaste”. Here the audience will learn com-
Inulins, Nutrients and Minerals. modity nutrients and minerals found in wild chicory
are high value and aid most of the bodies` growth
Terpenes are notorious for their analgesic, anti-in- and basics process of survival. Though the trigger-
flammatory, anti-bacterial and anti-fungal proper- ing of sound and video loops the diversity these mol-
ties, properties that can be used for new medicinal ecules sensory characteristics is also featured.
compounds. This is why they resist dangerous path-
ogenic and fungi so well in the soil. Inulins are prebi- The result is a haptic media artwork, that bio-mim-
otic fiber-based molecules and aid in the production ics the health benefits of the chicory plant.
INSPIRATION FOR THE TWO 3D PRINTED MODELS OF THE OLFACTOY BULB AND THE GUSTOTARY
SYSTEMS COMES FROM A SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS OF THE TO SENSES AND HOW THEY COMBINE
TO MAKE FLAVOR.AFTERTASTE: THE MOLECULAR ORCHESTRA
H O W TO P L AY T H E M O L E C U L E S
A root like chicory has more that 5 families of molecules. In Aftertaste the goal is to
expolore the health benefits for humans of 24 moleucles are found in the Chicory
Plant.
These molecules are also found in many other wild roots or “tubers” as they are called
in indegous cultures. Eating and cultivating more wild plants like Chicory help us to
create diversity and add more benefits to our diet.
The Audience plays the role of the Air: transporting the molecules from the nasel cav- 1.
ity to the human tongue. PICK THE MOLECULE FROM THE CHARGING STATION.
2.
TURN IT TO HEAR THE SOUNDS OF DIFFERENT FAMILIES OF SOUNDS
LIKE IN A TRADITIONAL ORCHESTRA.
2 µm
THE 3D PRINTED DESIGN IS BASED ON THE SCANNING ELECTRONIC MICROSCOPE IMAGES OF
INULIN POLLEN A MOLECULE THAT TRAVELS ON THE WIND IN THE SEEDS.
3.
SCREW IT INTO THE TONGUE TO HEAR THE BODY SOUNDS
AND DISCOVER EACH ONE’S HEALTH BENEFITS.
4.
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN YOU TURN IT UPSIDE DOWN AND
PLACE IT ON THE OLFACTORY BULB SCULPTURE?
5.
EXAMPLES: MOLECULES, FAMILEIS AND HEALTH BENEFITS. ...OR PLACE IT BACK IN THE CHARGING STATION.
WILD CHICORY (CICHORIUM INTYBUS): IN CULTIVATION AT SENSUS, THE NETHERLANDS. ACTION: TRANSPORT THE MOLECULES, MATCH THE FAMILIES AND FIND OUT WHAT THESE MOL
ECULES CAN DO FOR YOU!AFTERTASTE: THE MOLECULAR FAMILIES
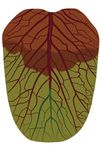
IN A MODEL WILD PLANT CHICORY (Cichorium intybus)
TERPENES PHENOLICS INULINS NUTRIENTS MINERALS
Terpenes are families that pro- Phenolics are families that help Inulins are families that are the Nutrients are families that help Minerals are families that are also
vide a plant with a natural defence a plant to grow and protect it basic fibers of growth for a plant. a plant grow strong and survive. essential for growth processes
system. The wild plant version of against toxins. They taste bitter Chicory is rich in pre-biotic fibers They also regualte our growth in the plant. In humans they also
chicory contains particuar terpe- The most famous phenolic of the and alternative sugars that taste processes and promote good preserve vital functions.
nes that smell strong and taste wild chicory plant is coffee. For sweet and promote energy levels, blood circulation and repair mus- Some actually help you taste and
bittter. They are currently being humans they boost free radicals as well as promote the grothe of cle tissue. They have a variety of smell, others create strong bones,
explored for applications in med- in the body to fight toxic invasions good bacteria which help to build smells and tastes that make chic- teeth and muscle tissue. There
icine particularly cancer, candita and act as an anti-inflamatory. your immune system. ory unique. are many more examples!
and bacterial infections.
EXAMPLES EXAMPLES EXAMPLES EXAMPLES EXAMPLES
Lactucopicrin oxalate Chicoric acid Short-chain inulin Crude Protein Zinc
Lactucin 3,5- Dicaffeoylquinic acid Long-chain inulin Free amino acids Calcium
Lactucopicrin Chlorogenic acid Oligofructose Plant fatty acids Magnesium
Dihydrolactucin Caftaric acid Sucrose Other Food Fibers Iron
Lactucin-oxalate Glucose DNA
8-deoxylactucin oxalate
Analgesic Anti-oxidant
Lactucopicrin oxalate Anti-inflammatory Chicoric acid
Anti-bacterial
Anti fungal 3,5-Dicaffeoylquinic
Lactucin
acid
Lactucopicrin Chlorogenic acid
Dihydrolactucin Terpenes Phenolics Caftaric acid
Lactucin-oxalate bitter bitter
8-deoxylactucin
Chicory molecules
oxalate sweet
Commodity
Inulins DNA
Nutrients
(present in all plants)
Food fibers:
Short-chain inulin sucrose
cellulose, hemicelulose
Mineral Examples Plant fatty acids
Long-chain inulin fructose
Zinc, Calcium, and lipids
Magnesium, Iron
glucose Proteins and free
amino acids
Gut health Growth and basic processes
CREDITS FOR AFTERTASTE
ARTIST Jill Scott
3D MODELS Natascha Jankovski
SOUND DESIGN & ELECTRONICS Vanessa Barrera Giraldo
ANIMATION & GRAPHICS Natascha Jankovski • Jasmine Chastonay
CONSTRUCTION HELP Raffaele Grosjean
PROGRAMMING Nikolaus Völzow • Vanessa Barrera Giraldo
ADVISORS CHIC LABS • Industrial Biotechnology Helsinki (Finland) • VTT Technical Research Centre
of Finland Ltd • Wageningen University Research WUR • KEYGENE Wageningen • SENSUS Roosendaal
(The Netherlands)
SCIENTIFIC CONSULTANTS Prof. Dr. Stephan Neuhauss (Institute for Molecular Biology –
Neurobiology UZH) • Sylvie Cuperus (Head of Life Science Zurich UZH, Switzerland)
THANKS TO Marille Hahne • 3D Hubs • Olav Leverik • Annette Bütsch • Thomas Zirlewagen •
Wanis Saad Ahmed El WgaliYou can also read