The Australian COVID-19 Vaccine Program - Women's Health ...
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
The Australian
COVID-19 Vaccine
Program
Womens Health Tasmania
Professor Katie Flanagan
President-Elect of the Australasian Society for
Infectious Diseases
Head of Infectious Diseases, LGH, Tasmania
Director of Tasmanian Vaccine Trial Centre
Clinical Professor, UTAS
Adjunct Professor, RMIT
Adjunct Assoc Prof, Monash University• Member of the Australian Technical Advisory
Group on Immunisation (ATAGI)
• Lead of ATAGI COVID-19 Vaccine Utilisation
and Prioritisation Working Group
Declarations
• Previous advisory board member for Seqiris
and Sanofi Pasteur
• Note these are my views and not necessarily
those of ATAGICOVID-19 Global Overview • Over 160 million documented cases of COVID-19 • Almost 3.4 million deaths • 184 vaccine candidates in pre-clinical development • 100 in human clinical trials
Replicating viral vector Non-replicating viral vector Viral-vector (e.g. measles) (e.g. adenovirus) vaccines Pros • Safe and well-tolerated • High protein expression & single dose often sufficient Cons • Scale-up takes time • Anti-vector immunity hampers response
RNA Vaccines
Non-replicating mRNA
Most common and simple
Self-amplifying mRNA
Contain genetic replication
machinery so can express more
protein for longer
Pfizer and Moderna vaccines are
non-replicating mRNA vaccines
Jackson et al. Vaccines 2020RNA Vaccines Pros • Easy to design • Rapid to manufacture and scale-up (within weeks of sequence identification) • Robust immune response Cons • Rapidly degraded therefore need packaging e.g. LNPs • Often require ultra-cold temperature storage • Stimulate a strong innate immune response / high AE profile • Limited data on repeat administration
Number in Number in
VACCINE PLATFORM Pre-Clinical Trials Clinical Trials
Live attenuated virus 2 1
Inactivated whole virus 9 15
Protein / peptide subunit 70 31
Platforms Non-replicating viral vectors 22 13
in Clinical (VVnr + APC) (0) (1)
Trials Replicating viral vectors 19 4
07 May 2021 (VVnr + APC) (0) (2)
DNA 16 10
RNA 24 15
Virus like particle (VLP) 17 5
Live attenuated bacterial vector 2 0
Replicating bacterial vector 1 0
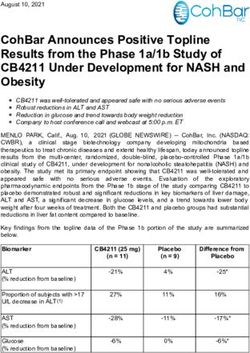
https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-candidate-vaccinesInterim Phase 3 Trial Results
Candidate Trial Details 1° Endpoint Priority Population Data / Notes Reference
BNT1621b N=43,661 95% efficacy against symptomatic disease 94% efficacy in those >65 yrs and those with prior COVID Polack et al
RNA 2 doses @ 0 and 4wks from 7d after dose 2 (COVID naïve) Consistent protection across age, gender, race, ethnicity, stable NEJM
BioNTech/Pfizer co-morbidities Dec 2020
1 severe case in vaccine recipient
mRNA-1273 N=30,000 94.1% efficacy against symptomatic No severe disease in vaccinated gp Baden et al
RNA 2 doses @ 0 and 4wks disease 37% participants from racial / ethnic minorities NEJM
NIH/Moderna Dec 2020
AZD1222 N=10,000 (Brazil) 70.4% combined efficacy No hospitalisation/severe disease in vaccine recipients Voyseyet al
Chimp 2 doses @ 0 and 4wks Brazil 64% efficacy from 14d after dose 2 Small numbers in >56y gp and those with co-morbidities Lancet
adenovirus N=12,390 (UK) UK 90% efficacy from 14d after dose 2 Greater efficacy with greater dosing interval Dec 2020
Astra Zeneca ½ dose then full 4wks
Johnson & N=43,783 66% overall against mod/severe 28d after Single shot vaccine, good efficacy across age groups Sadoff et al
Johnson vaccination 85% efficacy against severe disease NEJM
Ad26.COV2.S 100% efficacy against hospitalisation and death Apr 2021
Gamaleya N=21,977 >18yrs 91.6% effective from 21 days after dose 1 >90% effective in all age strata, 11% >60yrs, 98.5% white Logunov et al
Sputnik V Lancet
Ad26 / Ad5 Feb 2021
Novavax N=15,000 (UK) UK 89.7% efficacy against PCR+ No severe cases in UK vaccinated, 27% >65yrs Not published
S+Matrix M N=4,400 (S Africa) symptomatic disease in 18-84y olds
NVX-CoV2373 (COVID naïve)
Sinovac/Sinopharm/CanSino inactivated vaccines 50%, 79%, 66% efficacy respectivelyWarning! • The released phase 3 results are interim • Trials of different vaccines cannot be compared • Duration of protection and rate of immunity waning unknown • Priority populations under-represented and some not at all (pregnant women, severely immunosuppressed) • Limited data about effects on disease transmission • Rare side effects may be missed • Real-world efficacy may not be the same as observed in a clinical trial
Real-world
effectiveness
Data summary from Public Health EnglandWorldwide Rollout
• 11 vaccines with regulatory approval:
✓ 2 RNA – Pfizer; Moderna
✓ 4 viral vector – AstraZeneca/Oxford; Cansino
Ad5nCoV; Gameleya Sputnik V; Johnson &
Johnson
✓ 2 protein vaccine – Novavax; EpiVacCorona
(Russia)
✓ 3 inactivated virus – Sinovac; Sinopharm;
BBV152B (Bharat)
• More than 1.3 billion doses now given across
175 countries
(world = 195 countries & 7.8 billion people)
• Will still take years to cover 75% of world population
with 2 doses at this rate
https://www.Bloomberg.com/graphics/covid-vaccine-
tracker-global-distributionUsual Process COVID Vaccine Process
Australian COVID Initiation of Sponsor application to Australian government with
process TGA and PBAC advice from SITAG
Vaccine Program Direct discussions with
manufacturers
• Multiple gov departments: Regulatory TGA with advice from ACV TGA with advice from ACV
National Cabinet; National COVID-19 decisions
Coordination Commission; Gov COVID-19
Taskforce; Advisory Committee on Vaccines
(ACV); Australian Technical Advisory Group on
Immunisation (ATAGI); Therapeutic Goods Purchasing Australian Government Australian Government with
Administration (TGA); Science and Industry decisions with advice from PBAC advice from SITAG
Technical Advisory Gp (SITAG); Natl Centre for
Imm Research & Surveillance (NCIRS) Clinical and Statements from ATAGI Multiple providers including
technical with support from NCIRS ATAGI statements, NCIRS,
information training materials
• ATAGI COVID-19 Vaccine Advisory Groups
contracted by
• Vaccine utilisation & prioritisation
Commonwealth
• Vaccine distribution & program
implementation
• Vaccine safety, evaluation, monitoring Program Immunisation Branch in COVID vaccine Taskforce in
and confidence implementation conjunction with conjunction with
jurisdictions jurisdictionsPlatform Vaccine Developer Pre- Approval Notes
Company purchase Status
Doses
Chimp COVID-19 Oxford Uni 53.8 million PA with Local manufacturing
adeno Vaccine / Astra TGA ongoing at CSL
Australian AstraZeneca Zeneca 6m in fridge
Government mRNA BNT162b1
Comirnaty
BioNTech/ 40 million PA with
Pfizer TGA
Import only
-70°C storage / dry ice for
Commitment mRNA mRNA-1273 Moderna 25 million Not
shipping, 5d in fridge
Import only but potential
applied to for future on shore
Population Protein NVX-CoV2373 Novavax 51 million
TGA yet
PD with
manufacture
Import only
~25 million TGA Fridge storage
Human Ad26.COV2.S Johnson & Nil PD with Can be single dose
adeno Johnson TGA Fridge storage
Protein S-clamp UQ
TRIALS ABANDONED DUE51TO
million Phase 1 Government agreement to
FALSE POSITIVE HIV RESULTS
manufacture locally
PD = Provisional determination to be eligible to apply for provisional registration
PA = Provisional approval – valid for 2 yearsComirnaty COVID-19 Vaccine
Astra Zeneca
≥16 yrs ≥18 yrs
Two i.m. doses at least 21 days Two i.m. doses 12 weeks
Australian apart apart (can be 4-12 wks)
COVID-19 vaccine
recommendations Minimum interval 19 days Longer interval probably
Complete course within 6 wks better so aim for 12 wks
Preferred vaccine for thoseCOVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca and TTS • TTS = Thrombosis Thrombocytopenia Syndrome • Occurs 4-28 days post-vaccination • Clots in unusual sites e.g. brain with low platelet count and bleeding • Idiosycratic and no predisposing factors have been identified • Benefit / risk analysis performed taking into account low COVID-19 rates in Australia • TTS more common in younger people • COVID-19 complications / severity / death greater in older people • ATAGI recommended giving Comirnaty rather than AZ to those
Question Ans
Are there any known predisposing medical risk No (but more
factors for TTS common in
younger people)
Can I have AZ vaccine if I have a previous history of Yes
DVT / PE / CVA / ITP / thrombocytopenia
FAQs about Can I have AZ vaccine if I have risk factors for DVT / Yes
PE / CVA
AstraZeneca Can I have AZ vaccine if I have autoimmune
disease, cancer, immunocompromising condition?
Yes
Vaccine Can I have AZ vaccine if I’ve recently had heparin? Yes
Can I have heparin or surgery shortly after AZ Yes
vaccine?
Can I have AZ vaccine if I had TTS from first dose? No
Can I have AZ vaccine if have previous HIT, CVST, No (although no
splanchnic vein thromboembolism of unknown evidence to
aetiology? support this)• It is not currently recommended to give influenza
vaccine or any other vaccine on the same day as
Comirnaty or COVID-19 Vaccine Astra Zeneca
• No data
Timing with • Makes AE attribution difficult
• Preferred interval between COVID vaccines and flu
influenza vaccine or any other vaccine is currently 2 weeks
• In some cases, the interval may be shortened, e.g.
vaccine & • Will lead to missed opportunity to receive either
vaccine
other • Imminent need to administer due to prevailing
epidemiology e.g. for flu and COVID-19
vaccines • If inadvertently given together:
• There is no need to repeat either vaccine
• AEs more likelyPregnancy &
breastfeeding
• Both groups excluded from clinical trials of COVID
vaccines
• Animal studies – no evidence of harm
• No theoretical safety concerns (not a live
vaccine)
• Comirnaty the preferred vaccine for pregnant women
• Considered safe for breastfeeding women and babies
• Not routinely recommended in pregnancy, but not
contraindicated
• Consider individual risks and benefits of
vaccination
• Pregnant women with COVID-19 have worse
outcomesNew Variants and
Vaccine Immune Escape
• Pfizer/BioNTech BNT1621b (mRNA)
• Neutralises the UK B.1.1.7 variant but decreased
neut of B.1.351 S African and P.1 Brazilian variants
in vitro
• Oxford / AZ (Chimp adenovirus)
• 74.6% efficacy ag UK variant
• 10.4% against SA variant (symptomatic infection)
• Novavax NVX-CoV2373 (Protein/Matrix M)
• 86.3% efficacy against UK variant (50% of cases)
• 96.4% efficacy against wild-type strain
• 60.1% efficacy against S African variant if HIV-
• 48.6% if combine HIV- and HIV+ gps
100% against severe disease
• Currently making vaccines for variants, will
commence clinical trials Q2 this year
• Janssen Ad26.COV2.S (viral vector)
• 57% efficacy & 85% against hospitalization
with South Africa variant
66% efficacy in Latin America
(variants not specified)Summary • 11 vaccines deployed worldwide and >1 .3 billion doses given • Provisional approvals based on interim phase 3 safety and efficacy analyses • Many using new platforms never licensed for human vaccintion • Australia has two safe and effective vaccines and 2 more in the pipeline • First-generation vaccines will not be perfect and future vaccines will need to protect against emerging SARS-CoV-2 variant strains
You can also read