A MULTI-COLOR PANEL OF NOVEL LENTIVIRAL "GENE ONTOLOGY" (LEGO) VECTORS FOR FUNCTIONAL GENE ANALYSIS
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
Original publication: Molecular Therapy (2008); 16 4 698–706
http://www.nature.com/mt/journal/v16/n4/abs/mt20086a.html, doi:10.1038/mt.2008.6
Received 10 August 2007; accepted 2 January 2008; advance online publication 12 February 2008.
Authors’ website: http://www.LentiGO-Vectors.de
A multi-color panel of novel lentiviral “gene ontology” (LeGO) vectors for
functional gene analysis
Kristoffer Weber1,2,3, Udo Bartsch4, Carol Stocking2 & Boris Fehse1,3
1
Clinic for Stem Cell Transplantation, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, 20246 Hamburg, Germany. 2AG Molecular Pathology,
Heinrich-Pette-Institute, 20206 Hamburg, Germany. 3Experimental Pediatric Oncology and Hematology, University Hospital of the Johann
Wolfgang Goethe-University, 60590 Frankfurt am Main, Germany. 4Eye Clinic, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, 20246
Hamburg, Germany.
Correspondence should be addressed to:
Boris Fehse (b.fehse@kinderkrebsstiftung-frankfurt.de), Experimental Pediatric Oncology and Hematology, University Hospital of the Johann
Wolfgang Goethe-University, D-60590 Frankfurt am Main, Germany, phone: +49-69-678665-57
or Carol Stocking (stocking@hpi.uni-hamburg.de), AG Molecular Pathology, Heinrich-Pette-Institute, PO Box 201652, D-20206 Hamburg,
Germany.
Author contributions: K.W. designed, cloned and tested all constructs. U.B. developed and performed experiments with neural stem cells.
C.S. initiated the project and together with B.F. further developed concepts and advised the work of KW. B.F. wrote the first draft of the
manuscript.
ABSTRACT have found broad application as convenient gene transfer
Functional gene analysis requires the possibility of over- instruments ensuring stable cDNA expression [1,2]. Derived
expression, as well as down-regulation of one, or ideally from viruses belonging to the lentivirus genus of complex
several, potentially interacting genes. Lentiviral vectors retroviruses, they allow the efficient transduction of various
are well suited for this purpose as they ensure stable target tissues, including non-cycling cells and developing
expression of cDNAs, as well as shRNAs, and can zygotes [1,3]. Moreover, they facilitate introduction of short-
efficiently transduce a wide spectrum of cell targets when hairpin RNA (shRNA), which is processed into short-
packaged within the coat proteins of other viruses. Here interfering RNA (siRNA), for specific suppression of a gene
we introduce a multi-color panel of novel lentiviral “gene of interest [4]. The simultaneous introduction of (various
ontology” (LeGO) vectors designed according to the combinations of) different vectors is an interesting option for
"building blocks" principle. Using a wide spectrum of analyzing intracellular networks. Important applications
different fluorescent markers, including drug-selectable would be investigating the role of transcription factors
eGFP- and dTomato-blasticidin-S resistance fusion during development and differentiation, or the combinatorial
proteins, LeGO vectors allow simultaneous analysis of effects of genetic lesions in malignant transformation [5,6].
multiple genes and shRNAs of interest within single, In order to obtain unequivocal results in dual-transduction
easily identifiable cells. Furthermore, each functional protocols, gene-modified cells should be clearly identifiable.
module is flanked by unique cloning sites, ensuring Although many fluorescent markers are available [7], only a
flexibility and individual optimization. The efficacy of limited number have been incorporated into lentiviral
these vectors for analyzing multiple genes in a single cell vectors. Furthermore, expression levels of marker genes are
was demonstrated in several different cell types, often hampered in more complex vector designs.
including hematopoietic, endothelial and neural stem and Here we introduce a “multi-color” panel of lentiviral
progenitor cells, as well as hepatocytes. LeGO vectors vectors designed according to the Lego® "building blocks"
thus represent a valuable tool for investigating gene principle. Each vector allows expression of one transgene of
networks using conditional ectopic expression and knock- interest and/or a shRNA of choice and, in addition, a
down approaches simultaneously. fluorescent marker protein for identification and/or selection
of transduced cells. To permit simultaneous analysis of
INTRODUCTION multiple genes, a large spectrum of fluorescent marker genes
Completion of the human (and other) genome projects has has been used, including eGFP/BSD and dTomato/BSD
stimulated renewed interest in defining gene function. fusion genes, which combine the advantages of both
Functional genomic technologies, such as gene knock-outs fluorescent and drug-selectable marker genes. We show that
or transgenic models, are essential tools to fulfill this task. At these vectors are useful for concurrent over-expression as
the same time, the relevance of single gene approaches is well as suppression of various genes, thus allowing gene
often limited since gene functions may depend on complex function studies in a variety of target cells. In accordance
protein interactions and network structures. Therefore novel with their design and envisioned application for analysis of
techniques aimed at the simultaneous exploration of various gene networks, we have named our constructs Lentiviral
genes by either ectopic expression or targeted down- “Gene Ontology” (LeGO) vectors.
regulation are of great interest. Lentiviral vector systems
1RESULTS All current LeGO vectors are listed at http://www.LentiGO-
Development of Lentiviral Gene Ontology vectors (LeGO Vectors.de.
vectors)
In order to establish efficient tools for analyzing gene
a
functions and networks, our aim was to develop a novel set
LentiLox3.7 SIN-LTR Ψ RRE cPPT Ω
of lentiviral vectors that permit 1) efficient transfer and U6 CMV eGFP wPRE SIN-LTR
expression in a wide spectrum of cell types; 2) functional
and simultaneous analysis of both gene expression and
silencing; 3) efficient and versatile "tracking" methodology, LeGO‐G SIN-LTR Ψ RRE cPPT U6 Ω SFFV eGFP wPRE SIN-LTR
allowing the unequivocal identification of cells transduced
with one or multiple vectors; and 4) flexibility, as with LeGO‐G2 SIN-LTR Ψ RRE cPPT SFFV eGFP wPRE SIN-LTR
"building blocks" – facilitating the exchange of expression
cassettes using a defined combination of restriction enzymes LeGO‐iG2 SIN-LTR Ψ RRE cPPT SFFV IRES eGFP wPRE SIN-LTR
identical for each vector.
To fulfill these requirements, we redesigned a LeGO‐iG SIN-LTR Ψ RRE cPPT U6 Ω SFFV IRES eGFP wPRE SIN-LTR
previously published third-generation lentiviral vector
(LentiLox 3.7) [4]. Third-generation lentiviral vectors do not b
encode any viral proteins but contain cis-active elements for LeGO-G SIN-LTR Ψ RRE cPPT U6 Ω SFFV eGFP wPRE SIN-LTR
packaging, reverse transcription and integration [2]. This
design not only incorporates safety features, but also XbaI HpaI XhoI NotI BamHI EcoRI
provides space for up to 9 kb of foreign sequences. The
original LentiLox construct contains an RNA pol-III
LeGO-iG SIN-LTR Ψ RRE cPPT U6 Ω SFFV IRES eGFP wPRE SIN-LTR
promoter of the U6 RNA gene for the expression of shRNAs
and the cytomegalovirus (CMV) pol-II promoter, driving the
XbaI HpaI XhoI BamHI EcoRI StuI NotI MscI BsrGI
expression of the eGFP marker gene (Fig. 1a). The shRNA
Compatible with pSUPER
expression cassette is flanked by unique cloning sites that Cassette (XbaI/XhoI) H1 Ω
allow either the simple swamping of shRNA cassettes from
the pSUPER system developed by Brummelkamp and c
EmGFP eYFP tdTomato mCherry
colleagues [8] or the deletion of the cassette entirely (Fig. Current LeGO marker genes
eGFP Venus dsRed2 dsRedEx
1a).
mCerulean eGFP/BSD dTomato/BSD
To facilitate the use of the vector for simultaneous
transgene expression (in addition to the marker gene) and to Figure 1: The LeGO vector principle. (a) The initial construct
ensure higher expression levels in a wide spectrum of cell (LeGO-G) was derived from pLentiLox3.7 [4]. The first group of
types, several changes were made (Fig. 1a). In a first step, “LeGO-G” type vectors all express eGFP, either as a single,
the CMV promoter in the original construct was replaced removable (using the loxP/Cre system) marker gene to ensure
with the retroviral enhancer/promoter of spleen focus- efficient detection (e.g. LeGO-G and LeGO-G2) or in conjunction
with a gene of interest via an IRES (LeGO-iG2 and LeGO-iG). The
forming virus (SFFV), which has a broad and high
most sophisticated construct LeGO-iG allows co-expression of a
expression pattern, especially in cells of the hematopoietic gene of interest and an shRNA of choice together with the
compartment [9]. Next, an encephalomyocarditis virus fluorescent marker. (b) Based on the modular design of LeGO
(EMCV) internal ribosome entry site (IRES) [10], preceded vectors and the inclusion of single restriction sites, any element of
by unique cloning sites, was introduced in front of the interest can easily be removed or replaced by a related structure in
marker gene to facilitate co-expression of a transgene the master constructs. In particular, the shRNA cassette can directly
directly behind the SFFV promoter. Since a gene located be exchanged with a pSUPER cassette using XbaI/ XhoI cloning.
behind the IRES is expected to be translated with lower (c) All basic constructs (e.g. LeGO-G), in addition to several others,
efficiency than the one in front, such conformation ensures are available with the 11 listed (fluorescent) marker proteins. CMV,
cytomegalovirus enhancer/promoter; cPPT, central polypurine tract;
high-level expression of the transgene to be investigated
EmGFP, emerald green fluorescent protein; eYFP, enhanced yellow
(rather than the marker gene). In all vectors, the SFFV- fluorescent protein; RRE, rev-responsive element; SFFV, spleen
promoted expression cassette is flanked by loxP sites to focus-forming virus enhancer/promoter; SIN-LTR, self-
allow excision after introduction of the CRE recombinase. inactivating-long-terminal repeat; MCS, multiple cloning site;
Finally, the above configuration was used to develop wPRE, Woodchuck hepatitis virus post-transcriptional regulatory
a panel of vectors, each expressing a different marker gene. element.
As we wanted to use these vectors in a variety of cell
systems, but also have the option of using several vectors LeGO vectors could be produced at high titers and
simultaneously, a battery of 11 different fluorescent markers facilitate transduction of various cell types
were used (Fig. 1c) – each with its distinct advantages and Using a variety of different cell lines and primary cells, we
disadvantages in fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) confirmed that the vector panel described above allows
and fluorescence microscopy [7]. In addition, to also take efficient marking of transduced cells. First we established
advantage of the selection pressure and efficiency of in vitro that the SFFV promoter provided higher expression levels of
drug selection, we generated fluorescent fusion proteins the marker gene, particularly in blood cells, as compared to
coupled with a deaminase that confers resistance to the original CMV promoter (Fig. 2a). We then tested the
Blasticidin-S. An overview of the different vectors, which different fluorescent markers to assess whether expression is
we call Lentiviral Gene Ontology (LeGO) vectors in accord sufficient to ensure detection by fluorescence-activated cell
with the "building-block" design, is given in Fig. 1a and b. sorting (FACS) and fluorescence microscopy. An exemplary
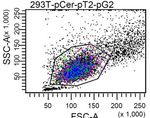
analysis of the expression of five different reporter genes in
2293T cells is illustrated in Figures 2b and c. Although there the United States) obtained titers between 30 × 106 and 60 ×
are significant differences in the mean fluorescence intensity 106 transducing units per ml for LeGO-G2 packaged with the
(MFI) between the different fluorescent markers (which G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV-G). More
reflects the different characteristics of the used fluorescent complex constructs including internal ribosome entry sites
proteins [7]), all markers were well detectable using standard (IRES) and shRNA cassettes were generated at titers >106
FACS devices. In Fig. 2b we present plots showing low to TU per ml on a regular base.
intermediate gene transfer rates associated with low-copy To directly address the actual impact of the vector
number vector integrations [11]. Nevertheless, the used design on infectious titers, we produced in parallel a panel of
markers allowed clear discrimination of transduced cells. nine different LeGO vectors in 293T cells. Titers obtained
Also, gene-modified cells were well identifiable by for the monocistronic LeGO-G vector (titer range of 3-4 x
fluorescence microscopy (Fig. 2c). Similar results were 107 per ml) were set as 100% and the relative titers of all
obtained for Ba/F3 cells (data not shown). It is important to other constructs were calculated. All measured titers were
note, that the detectibility of some colors may be further >106/ml, independently of the LeGO construct (Table 1),
improved on both flow cytometers and fluorescence albeit a significant influence of vector complexity and the
microscopes, by using optimized filter sets and/or suitable used marker gene was noted. As shown in Table 1, titers of
lasers [7]. LeGO vectors bearing an IRES were up to seven times lower
than those of comparable monocistronic constructs. Also,
a BaF3 LentiLox3.7 10
specific marker genes (e.g. tdTomato) may have some
BaF3 LeGO-G CMV-Enhancer/Promoter
8 SFFV-Enhancer/Promoter deleterious impact on vector titers (Table 1, compare also
Relative MFI
eGFP
eGFP
6
Fig. 2b). Thus, for more sophisticated vector constructs, it is
4
2
important to choose optimal marker genes to ensure clear-cut
0 identification of transduced cells.
FSC-H FSC-H 2 4
Days after transduction
b 293T LeGO-Cer 293T LeGO-G 293T LeGO-V 293T LeGO-T 293T LeGO-C Table 1: Absolute and relative titers of different LeGO vectors to
39.4% 61.3% 50.8% 20.2% 37.3%
mCerulean
compare the influence of vector backbones (rows 1-4) and marker
tdTomato
mCherry
Venus
eGFP
genes (1, 5-9)
LeGO Titerb Relative
FSC-H Marker Gene
c d MFI: 24 2,697 78,645
vectora [106 TU/ml]c titer [%]
LeGO-Cer -G -V -T -C
30
G eGFP 37 100
20
G2 eGFP 31 84
10
100µm
101 102 103
eGFP
104 105 iG eGFP 5.0 14
Figure 2: Novel LeGO vectors with different fluorescent markers iG2 eGFP 6.3 17
allow efficient transduction and detection of gene-modified cells. G/BSD eGFP/BSD 27 74
(a) The SFFV promoter ensures significantly better transgene
expression in hematopoietic cells as compared to the CMV Cer mCerulean 19 51
promotor. Shown are FACS analyses of Ba/F3 cells transduced
with pLentiLox3.7 (2.4%) and LeGO-G (1.2%). At different time V Venus 24 66
points after transductions performed in triplicates, mean T tdTomato 6.5 18
fluorescence intensities (MFI) were determined as shown in the bar
graph. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (b) Marking with C mCherry 15 40
various LeGO vectors allows unequivocal identification of gene- a
For the nomenclature of LeGO vectors see Fig. 1.
b
modified cells. 50,000 293T cells were transduced with equal Mean of two independent experiments (each performed in duplicates).
c
amounts (1 µl) of LeGO vectors (-Cer, -G, -V, -T, -C) encoding the Produced and titrated in parallel on 293T cells. TU: transducing units.
fluorescent marker indicated at the Y axis of each plot. Resulting
gene transfer rates thus reflect the different titers obtained with Based on the routinely produced high titers of LeGO vectors,
different marker genes (compare Table 1). FACS analysis was the proportion of transgene-expressing cells could readily be
performed 7 days after transduction. Please note that sufficient adjusted from less than 1% to nearly 100% (Fig. 2d) using
resolution is obtained even at low gene transfer rates of about 30%, increasing amounts of vector supernatants. In line with this,
i.e. at one vector copy per cell. (c) 293T cells transduced as
gene transfer rates of >90% were achieved with non-
described under 2b (same vectors) were analyzed by fluorescence
microscopy 10 days after gene transfer. Pictures were taken using concentrated VSV-G-pseudotyped particles at MOIs of app.
an Olympus IX71 equipped with a color CCD camera. (d) 50,000 10 to 20 for almost all cell line applications after just one
CHO cells were transduced in 24-well-plates by spinoculation transduction round. For example, the following cell lines
(1000 xg at RT) in a total volume of 500µl. Based on the obtained derived from different organs and tissues were efficiently
gene transfer rates the CHO-specific titer was estimated to be 2 x transduced: HEK-293T, CHO, NIH-3T3, HepaRG, HepG2
107/ml. The data shown in the histogram plot indicates that very [liver], K-562, Ba/F3, Jurkat [blood], IMR5, SKNSH
high differences in expression levels (up to a factor of 30 based on [neuroblastoma] (complete data not shown).
the MFI) could be obtained after a single transduction round using As one would expect, increasing the MOI also
increasing amounts (0.1 – 300 µl) of LeGO-containing supernatant.
resulted in higher expression levels, which are a direct
consequence of the number of vector integrations [11]. This
To perform cell marking experiments, we produced different
was monitored for Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells based
LeGO vectors in 293T cells. High to very high titers were
on the MFI which ranged from 2,697 to 78,645 (Fig. 2d).
readily obtained for all monocistronic LeGO vectors. In fact,
These results show that LeGO vectors are also suitable for
we routinely (in three different laboratories in Germany and
3studying the impact of expression levels of a given gene on seen with eGFP/BSD, dTomato/BSD is also retained in the
cell physiology. cytoplasm (Fig. 3b).
As expected and previously shown with related
lentiviral constructs, the high vector titers allowed for
efficient transduction of a variety of primary cells. In fact, in
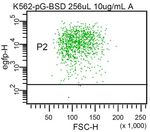
a K562 control pre-selection post-selection
K562 wt LeGO-G/BSD low LeGO-G/BSD low
cooperation with several groups, we have found very good to 9.2% 99.0% MFI: 16,642
excellent gene transfer efficiencies into different cell types.
For instance, with monocistronic LeGO-G (MOI: 1.8; please
note that the respective titer was determined on BaF/3 cells
which are app. 10 times less susceptible towards retroviral
transduction than 293T cells) we obtained 44% gene transfer
K562 wt LeGO-G/BSD high LeGO-G/BSD high
into primary human hematopoietic stem cells in vitro. More 91.9% 99.3% MFI: 41,048
than 90% transduction rates were obtained with LeGO-T2
(MOI: 20) and LeGO-G2 (MOI: 25) for primary human
endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) (Stockschläder M et al.,
manuscript in preparation). Murine primary hepatocytes have
been shown to be relative resistant towards lentiviral
transduction. Using spinoculation (1000 x g, 1 h, room b eGFP eGFP/BSD tdTomato dTomato/BSD
temperature), we were consistently able to transduce more
50µm
than 60% of freshly isolated murine hepatocytes with LeGO-
G2, albeit at comparatively high MOIs of about 80 (Benten
D, Weber K, Fehse B, unpublished data). Of note,
experiments with primary EPC and hepatocytes were
performed with single-round transductions using non- Figure 3: The eGFP/BSD resistance fusion protein ensures
efficient drug selection of transduced cells. (a) K562 cells were
concentrated supernatant.
transduced with a LeGO vector containing the eGFP-blasticidin
resistance (eGFP/BSD) fusion gene at low (upper panel, middle
The dual gene transfer markers eGFP/BSD and plot) or high (lower panel, middle plot) MOI. This resulted in 9.2%
dTomato/BSD facilitate selection of LeGO-transduced vs. 91.9% eGFP-expressing cells. Independent of the initial gene
cells transfer efficiency, Blasticidin selection resulted in an almost pure
Although LeGO vectors allow efficient selection of (≥99%) population of transduced cells (right panel). However,
transduced cells based on FACS, the latter may not always selected populations strongly differed in their transgene expression
be possible or desirable. To overcome this limitation, we levels (as illustrated by MFI), depending on gene copy number, i.e.
chose to couple a drug-selectable protein to the fluorescence the initial gene transfer frequencies. (b) 293T cells were transduced
with LeGO vectors encoding either the eGFP-blasticidin resistance
protein, to generate a dual transfer marker that should not
fusion or a standard eGFP gene (left two pictures). Remarkably,
interfere with the performance or flexibility of the vectors. In and in contrast to the standard eGFP, no green labeling of the cell
keeping with the "building blocks" approach, a cassette nucleus was observed with the fusion gene. Similarly, the tdTomato
containing the relatively small blasticidin-S deaminase but not the dTomato/BSD was able to enter the nucleus (right
(BSD) gene from Aspergillus terreus was generated which photographs). FSC, Forward scatter; SSC, side scatter.
transfers resistance to the antibiotic Blasticidin-S [12].
Moreover, the BSD gene sequence was modified to facilitate Multi-color detection of cells transduced with various
generation of analogous double markers for most of the LeGO-vectors
fluorescent proteins (EmGFP, EYFP, Venus, Cerulean, The main impetus behind establishing a multi-color panel of
tdTomato, and mCherry) present in the LeGO vectors using LeGO vectors was to permit the investigation of deregulated
a one-step cloning procedure (via the unique BsrGI-site). (ectopic and/or down-regulated) expression of several genes
Remarkably, there was only a limited reduction in in parallel in a single cell. To determine if LeGO vectors do
titers of LeGO-G/BSD as compared to LeGO-G vectors. indeed facilitate concurrent detection of several vectors,
Also, the MFI of eGFP expression was slightly reduced, but 293T cells were simultaneously transduced with three
a bright signal in FACS and microscopic analysis was still different LeGO vectors (LeGO-G2, LeGO-T2, LeGO-Cer).
readily detectable (Fig. 3a,b). Of note, the fusion to BSD All these marker genes are easily detectable using
seems to prevent entry of eGFP into the nucleus (Fig. 3b). commercially available flow cytometers with standard blue
Blasticidin-S selection of transduced cultures was highly 488 nm (eGFP, tdTomato) and violet 405 nm (Cerulean)
effective, resulting in almost pure eGFP-positive populations lasers and commonly used filter sets. Transduction rates
independently of the initial gene transfer frequencies, i.e. were adjusted to approximately 50% for each vector.
gene copy number (Fig. 3a). Thus, the novel dual eGFP/BSD Consequently, about 25% of the transduced cells should be
gene transfer marker not only allows convenient and double-positive with either transgene combination. Data
inexpensive in vitro selection of transduced cells, but it can shown in Figure 4a are in full agreement with this theoretical
also be used to adjust gene expression levels by prediction. Moreover, about 12.5% of the analyzed cells
administrating different vector doses before selection. could be expected to be transduced by all three LeGO
To prove whether the principle of dual gene transfer vectors. To verify this, eGFP-positive cells in the FACS
markers may be extended to other fluorescent proteins we analysis (P2 gate in the histogram plot) were re-analyzed for
next constructed a dTomato/BSD fusion protein. As with co-expression of Cerulean and tdTomato. Again, the
eGFP/BSD, the dTomato/BSD marker facilitates detection of percentage of triple-positive cells (13.5%) was in good
transduced cells by FACS and fluorescence microscopy as accord with the predicted value (Fig. 4b).
well as selection with Blasticidin-S (data not shown). As
4It is noteworthy that due to the non-optimal excitation by the transduced cells showed high eGFP expression levels (Fig.
blue laser, the fluorescence intensity of tdTomato is 5b, upper panel, boxes).
underestimated in flow cytometry. In contrast, when assessed As discussed above, performance of LeGO vectors is
by fluorescence microscopy with optimal green excitation dependent on the complexity of the vector genome.
light, tdTomato fluorescence appears even brighter than that Consequently, exploiting all possible expression cassettes of
of eGFP. As an example, 293T cells co-expressing eGFP and a given LeGO vector will usually result in lower titers and
tdTomato are depicted in Fig. 4c. expression levels as compared to monocistronic marking
vectors (compare Table 1 and Fig. 2). For more sophisticated
a LeGO-Cer+T2+G2 LeGO-Cer+T2+G2 LeGO-Cer+T2+G2 LeGO-Cer+T2+G2
vector constructs, it is thus important to choose optimal
25.2%
24.0%
21.4%
marker genes to ensure clear-cut identification of transduced
tdTomato
tdTomato
cells. In the experiment described here, the titer of the
eGFP
SSC-A
P1
complex construct LeGO-iT-tCD34-GFP2 was still high
enough (up to 5 x 106/ml as determined on K562 cells) to
FSC-A mCerulean eGFP mCerulean
obtain transduction efficiencies of >80% after a single
b LeGO-Cer+T2+G2 c transduction round with an MOI of app. 10 (Fig. 5a, left
LeGO-Cer+T2+G2 13.5% plots). At such transduction rates, tdTomato expression
tdTomato
40.6%
Count
levels were sufficient to identify transduced cells by FACS.
However, it should be noted that separation of gene-modified
eGFP
mCerulean
cells by flow cytometry was more efficient based on tCD34
detection using an APC-labeled antibody (Fig. 5a, right
Figure 4: Efficient multi-color marking with LeGO vectors. (a) plots).
293T cells were transduced with the vectors LeGO-Cer, LeGO-G2
and LeGO-T2 encoding Cerulean, eGFP and tdTomato
fluorescence marker proteins, respectively. MOIs were adjusted to a
ensure 40-50% transduction efficiency with each single vector. MFI: 27,390 MFI: 31,205
CD34-APC
tdTomato
Double-transduced cells are easily detectable. As expected, about Control
one quarter of the cells are co-expressing each of the possible
marker combinations. (b) To assess the percentage of cells
simultaneously expressing all three marker proteins, eGFP-positive
cells were gated (histogram plot) and reanalyzed with respect to the eGFP eGFP
co-expression of Cerulean and tdTomato. As seen in the dot plot,
MFI: 6,096
13.5% of all cells express all three fluorescent markers, which is in MFI: 5,796
CD34-APC
tdTomato
very good agreement with the expected frequency. (c) Fluorescence shRNA
‘GFP2‘
microscopy of the triple transduced 293T cells confirms marker
gene co-expression. An overlay for eGFP and tdTomato is shown,
revealing single- as well as double-positive cells. As clearly visible
eGFP eGFP
with the more optimal filters in the microscope, tdTomato MFI reduction: 77.7% 81.4%
fluorescence (exposure time: 250 ms) is even brighter that that of
eGFP (exp. time: 500 ms). b
LeGO vectors simultaneously allow efficient ectopic
Control
transgene expression as well as down-regulation of gene
expression in single cells
We next asked whether the novel vector system would, as
anticipated, simultaneously allow ectopic expression of a
shRNA
“gene of interest” while down-regulating a second. To ‘GFP2‘
address this question, a LeGO-iT-based “test” vector
(“LeGO-iT-tCD34-GFP2”) was designed containing the
following elements: the tCD34 gene[13] as the “gene of Figure 5: LeGO vectors facilitate simultaneous over-expression of
interest” to express, the tdTomato gene as a marker, and a one gene and down-regulation of another within single target cells.
pSUPER cassette containing an shRNA (“GFP2”) against the K562 cells expressing eGFP were transduced with tdTomato
eGFP gene, the target gene for suppression. A corresponding (LeGO-iT) vectors (compare Fig. 1 for nomenclature) expressing a
truncated CD34 gene (tCD34) as the “gene of interest” in
control vector (“LeGO-iT-tCD34-H1”) was constructed with
conjunction with an shRNA expression cassette, which was either
the same elements, including the H1 promotor, but lacking empty (= control vector: LeGO-iT-tCD34-H1) or contained an
the shRNA. shRNA directed against eGFP [27] (= vector LeGO-iT-tCD34-
K562 cells constitutively expressing eGFP were GFP2). (a) FACS analysis carried out 9 days after transduction
transduced with the test and the control vectors. As shows that both vectors conferred tdTomato and tCD34 positivity to
predicted, tdTomato-positive cells showed both a down- eGFP-K562 cells. In addition, transduction with the vector
regulation of eGFP and expression of tCD34. Indeed, 9 days expressing the shRNA against eGFP resulted in a strong
after transduction, tdTomato-expressing cells showed a circa suppression (app. 80% MFI reduction) of eGFP expression as
80% decrease in eGFP expression as compared to cells compared to cells transduced with the control vector. (b) These
results were also confirmed by fluorescence microscopy: eGFP-
transduced with the control vector, as assessed by the MFI
K562 cells transduced with the LeGO-iT-tCD34-H1 (“control”)
(Fig. 5a). Down-regulation of eGFP was also clearly became tdTomato-positive while still expressing eGFP (upper
detectable by fluorescence microscopy in shRNA- panel, examples are marked by boxes), whereas those cells
transduced, tdTomato-expressing cells (Fig. 5b, lower panel, transduced with the LeGO-iT-tCD34-GFP2 vector (“GFP2”) had
boxes). In contrast, non-transduced as well as control-vector- strongly down-regulated eGFP expression (lower panel, boxes).
5To further test the usefulness of our novel vectors, we Olig2 and Nkx2.2 were both easily detectable by
performed experiments using primary neural stems cells or immunofluorescence staining in the nuclei of tdTomato- and
NIH-3T3 fibroblasts, with the aim of simultaneously eGFP-positive NIH-3T3 cells whereas parental NIH-3T3
expressing two transcription factors. The helix-loop-helix cells did not express those transcription factors (Fig. 6).
transcription factor Olig2 and the homeodomain When NIH-3T3 cells were simultaneously transduced with
transcription factor Nkx2.2 play critical roles in the the two different LeGO vectors, cells co-expressing both
specification and maturation of the oligodendrocyte lineage, tdTomato and eGFP, as well as cells expressing only
respectively [14]. Forced expression of Olig2 has been tdTomato or eGFP, were detectable (Fig. 6i-l). For forced
shown to promote differentiation of neural precursor cells or co-expression of Olig2 and Nkx2.2 in neural stem cells, cells
embryonic stem cells into oligodendrocytes, and in were first transduced with LeGO-iT2-Olig2. Cells expressing
combination with Nkx2.2 to induce ectopic formation of tdTomato were then isolated by FACS and clonally
oligodendrocytes in the embryonic chick spinal cord expanded (Fig. 6m,q). Subsequent transduction with LeGO-
[15,16,17]. iG2-Nkx2.2 (Fig. 6 n,r) resulted in the presence of cells co-
For ectopic expression of Olig2 and/or Nkx2.2 in expressing both marker genes (Fig. 6m-t).
NIH-3T3 and neural stem cells, we generated the ecotropic
vectors LeGO-iT2-Olig2 and LeGO-iG2-Nkx2.2, encoding DISCUSSION
Olig2 together with tdTomato and Nkx2.2 together with A large repertory of different gene transfer vectors is
eGFP. Titers for both vectors were in the range of 3 to 5 x available for various types of research and for clinical
106 per ml. Using MOIs between 50 and 65 we were able to purposes. Those include viral and non-viral, integrating and
transduce more than 25% of the neural stem cells with Olig2 episomal vectors [18,19]. In particular, different lentiviral
and app. 50% with Nkx2.2, as estimated based on the vector systems have been developed and show excellent
detection of tdTomato and eGFP, respectively, by FACS performance for many applications [1,2,4]. We have
analysis. For LeGO-iT2-Olig2 gene transfer rates appeared redesigned a third-generation lentiviral vector, to create a
to be even higher when assessed by fluorescence flexible vector system that allows simultaneous expression
microscopy. and/or suppression of several genes in a single cell to
facilitate the analysis of gene networks. The strength of this
system lies in its versatility, allowing optimization for
various cell systems and different analytical applications.
To facilitate the use of lentiviral vectors in a wide
spectrum of cell types, two strategies can be employed. First
of all, transcription rates in specific cell types can be
improved by using universal strong promoters. In the LeGO
vector system, we replaced the CMV promotor in the
original LentiLox 3.7 vector with the SFFV promoter. This
indeed led to a much better transgene expression in primary
and established hematopoietic cells. In addition, the vectors
showed good to excellent performance in many different cell
lines representing various tissues (e.g. HepaRG, K-562,
Ba/F3, Jurkat, CHO, NIH-3T3, HEK-293T, IMR5, SKNSH),
but also in primary neural, hematopoietic and endothelial
stem & progenitor cells as well as hepatocytes. Secondly,
transduction efficiencies of various cell types can be greatly
improved by utilizing different envelope proteins for
pseudotyping. In addition to using the G protein of vesicular
stomatitis virus (VSV-G), the wild-type or altered env
proteins of other retroviruses (e.g. GALV, RD114, or even
Figure 6: LeGO vectors can be used for the concurrent expression ecotropic MuLV) can be used [20,21,22]. By using the most
of two transcription factors in neural stem cells. To establish the efficient infectious pseudotype for the given cell system, we
system, parental NIH-3T3 fibroblasts expressing neither Olig2 nor have obtained high to very high gene transfer efficiencies
Nkx2.2 were transduced with ecotropic pseudotypes of LeGO-iT2- into the above named primary and cultured cells. It is
Olig2 (a-d), LeGO-iG2-Nkx2.2 (e-h) or simultaneously both noteworthy that cooperation partners have shown efficient in
vectors (i-l). Immunocytochemical analysis of cultures two weeks vivo transduction of murine hematopoietic stem cells after
after transduction demonstrated expression of Olig2 (b) in
direct vector injection into the bone marrow (N. Drize and I.
tdTomato-positive (a) cells and expression of Nkx2.2 (f) in eGFP-
positive (e) cells (overlays of a, b and e, f are shown in c and g, Nifontova, Hematological Scientific Center, Moscow,
respectively). NIH-3T3 cultures concurrently transduced with both personal communication, 26 November 2007). In this
vectors contain cells co-expressing tdTomato and eGFP (arrows in context, the possibility of pseudotyping LeGO vectors with
i-l). Neural stem cells (m-t) were transduced with LeGO-iT2-Olig2, the ecotropic MuLV, as pioneered by Schambach et al. [22],
positive cells were isolated by FACS and clonally expanded (m,q). is particularly interesting since this allows experiments using
Subsequent transduction of neural stem cell clones with LeGO-iG2- mouse cells with lentiviral vectors under biosafety level-1
Nkx2.2 (n,r) resulted in the appearance of cells co-expressing containment.
tdTomato and eGFP (arrows in m-p; q-t is a higher magnification of To permit simultaneous expression and/or
a tdTomato/eGFP-positive cell shown in m-p). All cultures were
suppression of several genes in one and the same cell as a
counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (d, h, l, p, t). Bar in p (for a-p):
100µm ; in t (for q-t): 50µm. mean to facilitate the analysis of gene networks, LeGO
6vectors not only include expression cassettes for both METHODS
transgenes and shRNAs, but different vectors are detectable Cloning of LeGO vectors. Standard molecular cloning
within one single cell by using various marker genes. Other techniques were used to generate the LeGO vectors based on
potential applications for our multicolor vector system the plasmid pLentiLox 3.7[4]. All PCR-amplified elements
include the analysis of competitive survival of differently have been verified by DNA sequencing. Vector maps and
manipulated and gene-marked cells, e.g. after hematopoietic sequence data for all vectors are available at
stem cell transplantation [23], or studying interactions of http://www.LentiGO-Vectors.de. BSD was amplified from
different cell types in vivo, e.g. tumor and stroma cells. Vivid Colors™ pcDNA6.2/EmGFP-Bsd/V5-DEST
Overall, eleven different markers were included, (Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany). cDNAs for eGFP, eYFP,
detectable in five separate detection channels in suitable flow dsRed2, dsRedExpress (all from Clontech, Heidelberg,
cytometers. The marker genes used have been optimized by Germany), EmGFP (Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany),
a number of different groups [24,25,26], but nevertheless Cerulean [25], Venus [24], tdTomato and mCherry [26] were
unequivocal detection of gene-modified cells requires used as PCR templates. The used shRNA against eGFP was
sufficient expression of the marker gene. Using the SFFV previously described [27]. The EMCV-IRES was cloned out
promoter, we could show that transduced cells were easily of pMys-IG [28]. The SFFV enhancer/promoter was PCR-
detectable by flow cytometry, even with only one vector amplified out of pSF91-iGFP (R780) [5].
copy per cell. This may, however, vary between different
cell types, and other promoters may be substituted into the Generation of viral particles. Cell-free viral supernatants
LeGO vectors. were generated by transient transfection of PhoenixGP or
Importantly, our data also demonstrates that the 293T packaging cells as described [29], using the 3rd
panel of LeGO vectors indeed affords identification of cells generation packaging plasmids pMDLg/pRRE and pRSV-
transduced at the same time with two or more different Rev [2]. The following Env or G proteins were used:
vectors. The large spectrum of LeGO vectors available ecotropic MuLV [30], RD114/TR [21], GALV-C4070A, or
allows comparable experiments with any flow cytometer. A VSV-G [29]. Supernatants containing pseudotyped vector
single 488nm-laser for excitation permits the detection of particles were titrated using suitable target cells (ecotropic
three colors (e.g. eGFP vs. Venus vs. tdTomato). With two- MuLV: NIH3T3 cells; GALV-C4070A, RD114/TR, VSV-G:
laser FACS devices (and suitable filter sets), several 293T cells, if not stated otherwise). Initial gene transfer rates
combinations of up to four colors may be simultaneously were analyzed at least 48 hours after transduction by
detectable, for instance with 488 nm and 405 nm lasers, fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS). Titers of up to 9
Cerulean vs. eGFP vs. Venus vs. tdTomato. As exemplarily x 107 VSV-G pseudotyped virus particles (for LeGO-G2) per
shown for dual eGFP/BSD and dTomato/BSD genes, drug ml un-concentrated supernatants were obtained.
selection (Blasticidin-S) can facilitate selection of gene-
modified cells (containing just one vector copy), which can Cell culture and lentiviral gene transfer. All cells were
also be detected by flow cytometry. This concept may easily cultured in their respective growth media supplemented with
be extended to other fluorescent proteins. penicillin/streptomycin. For transduction, target cells were
The final requirement for the novel vectors was incubated at 1x105 /ml in the presence of 8µg/ml polybrene
flexibility. Since the vector is “just another tool” – it should and centrifuged at 1000×g for 1 hour at room temperature in
be easily adapted to particular experimental needs. Therefore the presence of viral supernatant at MOIs adjusted in
we designed the vectors according to the popular Lego® accordance with the experimental needs [29].
"building blocks" principle. Each LeGO vector consists of Neural stem cells were isolated from the cerebral
several modules, the promotor/enhancer, the transgene, the cortex of 14-day-old mouse embryos and expanded as
marker gene and the shRNA expression cassette, each of adherent cells on either gelatine- or Matrigel-coated cell
which can be easily replaced in the basic constructs using culture plastic in NS-A medium (Euroclone, Milan, Italy)
standard restriction enzymes. supplemented with modified N2, epidermal growth factor
An obvious concern for complex vector constructs and fibroblast growth factor-2 (both from Tebu, Frankfurt,
containing several expression cassettes is the question of Germany) [31].
sufficient vector titers. Indeed, titers for bicistronic LeGO
vectors (containing IRES) were significantly lower than for FACS and immunocytochemical analysises. FACS data
monocistronic vectors. However, even for the most were acquired using the following cytometers (all from
sophisticated constructs, the non-concentrated titers were Becton Dickinson, Heidelberg, Germany): FACSAria
usually >106 TU per ml, which should be sufficient for most (405/488/635nm lasers), FACSCanto (405/488/635nm
ex vivo applications. Concentrating vector supernatant, e.g. lasers) or FACSscan (488nm laser) equipped with default
by centrifugation, would further increase the infectious titer. filter sets. The FACSAria was also used for cell sorting. For
In conclusion, the LeGO vector system combines immunocytochemical analysis, cultures were fixed in PBS
numerous advantages – including efficient transfer and stable containing 4% paraformaldehyde, blocked in PBS containing
expression of transgenes as well as shRNAs in different 0.1% Triton and bovine serum albumin and incubated with
target cells to facilitate functional gene analyses. antibodies to olig2 (R&D Systems, Wiesbaden-Nordenstadt,
Incorporation of a wide panel of fluorescent markers (with or Germany) or Nkx2.2 (Developmental Studies Hybridoma
without drug-selectability) ensures identification of multiply Bank, University of Iowa, USA), followed by incubation
transduced cells. Finally, the modular LeGO design allows with appropriate secondary antibodies (Dianova, Hamburg,
quick adaptation to current experimental needs using Germany) and Hoechst 33258 (Sigma, Taufkirchen,
standardized cloning procedures. Thus LeGO vectors Germany).
represent interesting tools for the analysis of complex gene
networks in various in vitro and in vivo models.
7ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS site is not selected by a scanning mechanism. EMBO J; 9: 3753-
3759.
The authors thank their many colleagues for their kind 11. Kustikova O, Wahlers A, Kühlcke K, Stähle B, Zander A, Baum C,
support with various cells and constructs: François-Loïc et al. (2003). Dose finding with retroviral vectors: Correlation of
Cosset (INSERM, U758, Lyon, France) (RD114/TR), Gary retroviral vector copy numbers in single cells with gene transfer
P. Nolan (Department of Microbiology and Immunology, efficiency in a cell population. Blood; 102: 3934-3937.
12. Kimura M, Takatsuki A and Yamaguchi I (1994). Blasticidin S
Stanford University, Stanford, CA) (Phoenix packaging deaminase gene from aspergillus terreus (BSD): A new drug
cells), Winfried Beyer (Molecular Pathology, Heinrich-Pette- resistance gene for transfection of mammalian cells. Biochim
Institute, Hamburg, Germany) (VSV-G, gibbon ape leukemia Biophys Acta; 1219: 653-659.
virus-C4070A), Bettina Petrowitz (Eye Clinic, UMC 13. Fehse B, Kustikova O, Li Z, Wahlers A, Bohn W, Beyer W, et al.
(2002). A novel 'sort-suicide' fusion gene vector for T cell
Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) (murine Nkx2.2 manipulation. Gene Ther; 9: 1633-1638.
cDNA), and David H. Rowitch (Department of Pediatrics 14. Rowitch D (2004). Glial specification in the vertebrate neural tube.
and Institute for Regeneration Medicine, University of Nat Rev Neurosci; 5: 409-419.
California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA) (murine Olig2 15. Zhou Q, Choi G and Anderson D (2001). Bhlh transcription factor
Olig2 promotes oligodendrocyte differentiation in collaboration with
cDNA), Luk van Parijs (Department of Biology, Nkx2.2. Neueon; 31: 791-807.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA) 16. Copray S, Balasubramaniyan V, Levenga J, de Bruijn J, Liem R and
(pLentiLox3.7), Roger Y. Tsien (Howard Hughes Boddeke E (2006). Olig2 overexpression induces the in vitro
MedicalInstitute, University of California, La Jolla, CA) differentiation of neural stem cells into mature oligodendrocytes.
Stem Cells; 24: 1001-1010.
(tdTomato and mCherry cDNA), Atsushi Miyawaki (Brain 17. Du Z, Li X, Nguyen G and Zhang S (2006). Induced expression of
Science Institute, RIKEN, Wako-city, Saitama, Japan)/Timm Olig2 is sufficient for oligodendrocyte specification but not for
Schroeder (GSF-National Research Center for Environment motoneuron specification and astrocyte repression. Mol Cell
and Health, Neuherberg, Germany) (Venus cDNA), and Neurosci; 33: 371-380.
18. Lundstrom K (2003). Latest development in viral vectors for gene
David W. Piston (Molecular Physiology and Biophysics, therapy. Trends Biotechnol; 21: 117-122.
Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN) 19. Glover D, Lipps H and Jans D (2005). Towards safe, non-viral
(Cerulean cDNA). This work was supported by the Deutsche therapeutic gene expression in humans. Nat Rev Genet; 6: 299-310.
Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG-SPP1230 to B.F.), the 20. Stitz J, Buchholz C, Engelstädter M, Uckert W, Bloemer U, Schmitt
I, et al. (2000). Lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with envelope
Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF glycoproteins derived from gibbon ape leukemia virus and murine
01GN0501 to U.B.), the Deutsche Krebshilfe (to C.S.) the leukemia virus 10a1. Virology; 273: 16-20.
Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst (to K.W.) and the 21. Sandrin V, Boson B, Salmon P, Gay W, Negre D, Le Grand R, et al.
Frankfurter Stiftung für krebskranke Kinder. B.F.’s current (2002). Lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with a modified RD114
envelope glycoprotein show increased stability in sera and
position is funded by the Deutsche Krebshilfe. This work is augmented transduction of primary lymphocytes and CD34+ cells
part of the doctoral thesis of K.W. derived from human and nonhuman primates. Blood; 100: 823-832.
22. Schambach A, Galla M, Modlich U, Will E, Chandra S, Reeves L, et
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT al. (2006). Lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with murine ecotropic
envelope: Increased biosafety and convenience in preclinical
The authors declare no competing financial interests. research. Exp Hematol; 34: 588-592.
23. Fraser C, Szilvassy S, Eaves C and Humphries R (1992).
REFERENCES Proliferation of totipotent hematopoietic stem cells in vitro with
1. Naldini L, Blömer U, Gallay P, Ory D, Mulligan R, Gage F, et al. retention of long-term competitive in vivo reconstituting ability. .
(1996). In vivo gene delivery and stable transduction of nondividing Proc Natl Acad Sci USA; 89: 1968-1972.
cells by a lentiviral vector. Science; 272: 263-267. 24. Nagai T, Ibata K, Park E, Kubota M, Mikoshiba K and Miyawaki A
2. Dull T, Zufferey R, Kelly M, Mandel R, Nguyen M, Trono D, et al. (2002). A variant of yellow fluorescent protein with fast and efficient
(1998). A third-generation lentivirus vector with a conditional maturation for cell-biological applications. Nat Biotechnol; 20: 87-
packaging system,. J Virol; 72: 8463-8471. 90.
3. Pfeifer A, Ikawa M, Dayn Y and Verma IM (2002). Transgenesis by 25. Rizzo M, Springer G, Granada B and Piston D (2004). An improved
lentiviral vectors: Lack of gene silencing in mammalian embryonic cyan fluorescent protein variant useful for fret. Nat Biotechnol; 22:
stem cells and preimplantation embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA; 445-449.
99: 2140-2145. 26. Shaner N, Campbell R, Steinbach P, Giepmans B, Palmer A and
4. Rubinson D, Dillon C, Kwiatkowski A, Sievers C, Yang L, Kopinja Tsien R (2004). Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow
J, et al. (2003). A lentivirus-based system to functionally silence fluorescent proteins derived from discosoma sp. Red fluorescent
gene in primary mammalian cells, stem cells and transgenic mice by protein. Nat Biotechnol; 22: 1567-1572.
rna interference. Nat Genet; 33: 401-406. 27. Scherr M, Battmer K, Ganser A and Eder M (2003). Modulation of
5. Schwieger M, Löhler J, Friel J, Scheller M, Horak I and Stocking C gene expression by lentiviral-mediated delivery of small interfering
(2002). AML1-ETO inhibits maturation of multiple rna. Cell Cycle; 2: :251-257.
lymphohematopoietic lineages and induces myeloblast 28. Kitamura T, Koshino Y, Shibata F, Oki T, Nakajima H, Nosaka T, et
transformation in synergy with icsbp deficiency. J Exp Med; 196: al. (2003). Retrovirus-mediated gene transfer and expression cloning:
1227-1240. Powerful tools in functional genomics. Exp Hematol; 31: 1007-1014.
6. Modlich U, Kustikova O, Schmidt M, Rudolph C, Meyer J, Li Z, et 29. Beyer W, Westphal M, Ostertag W and von Laer D (2002).
al. (2005). Leukemias following retroviral transfer of multidrug Oncoretrovirus and lentivirus vectors pseudotyped with lymphocytic
resistance 1 (MDR1) are driven by combinatorial insertional choriomeningitis virus glycoprotein: Generation, concentration, and
mutagenesis. Blood; 105: 4235-4246. broad host range. J Virol; 76: 1488-1495.
7. Shaner N, Steinbach P and Tsien R (2005). A guide to choosing 30. Morita S, Kojima T and Kitamura T (2000). Plat-E: An efficient and
fluorescent proteins. Nat Methods; 2: 905 - 909. stable system for transient packaging of retroviruses. Gene Ther; 7:
8. Brummelkamp T, Bernards R and Agami R (2002). A system for 1063-1066.
stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. 31. Conti L, Pollard S, Gorba T, Reitano E, Toselli M, Biella G, et al.
Science; 296: 550-553. (2005). Niche-independent symmetrical self-renewal of a
9. Baum C, Hegewisch-Becker S, Eckert HG, Stocking C and Ostertag mammalian tissue stem cell. PLoS Biol; 3: e283.
W (1995). Novel retroviral vectors for efficient expression of the
multidrug resistance (MDR-1) gene in early hematopoietic cells. J
Virol; 69: 541-7547.
10. Kaminski A, Howell MT and Jackson RJ (1990). Initiation of
encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation: The authentic initiation
8You can also read