BBVA FOUNDATION-CNIO CANCER CELL BIOLOGY PROGRAMME
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
Vice-Direction of Basic Research BBVA Foundation-CNIO Cancer Cell Biology Programme
BBVA FOUNDATION-CNIO CANCER
CELL BIOLOGY PROGRAMME
ERWIN F. WAGNER Programme Director
The overall strategic goals of the BBVA Foundation-Cancer
Cell Biology Programme are to achieve a better understanding
“ Our main goal is to make
of the events leading to cancer development, progression and CNIO internationally
metastasis, and to discover molecular mechanisms that could more competitive
provide a basis for novel therapies. In March 2014, a Senior
Research CNIO Group, which was previously part of the Molecular
and that it remains an
Pathology Programme and headed by Francisco X. Real, joined international institution ;
our Programme. Our Groups investigate how a tumour can grow 15 different nationalities
as an ‘ extrinsic organ ’. The research covers various aspects of
tumour cell biology, ranging from tumour stem cells, tumour are represented in our
cell interactions with host cells/environment such as tumour- Programme. We aim to
associated cells like macrophages and fibroblasts, to the role of
inflammation, angiogenesis, as well as cell adhesion, metabolism
perform first-class cancer
and metastasis. Powerful state-of-the-art mouse genetic models, cell biology research and to
human cellular systems, high-throughput genomic/proteomic train students and postdocs
and biochemical tools, as well as patient-derived materials, are
employed. At present, these aspects are successfully covered
to become the next-
and integrated in an interactive and collaborative manner by the generation of promising
complementary research areas of 2 Senior and 3 Junior Groups. scientists.”
My own Research Group focuses on understanding the role of
the transcription factor complex AP-1 ( Fos/Jun ) in physiological
and pathological processes. We work on liver fibrosis and fatty
liver disease, inflammation and cancer, on bone homeostasis
and osteosarcomas, and also aim to molecularly define the
causes of skin cancer and inflammatory skin diseases, such as
psoriasis. Mirna Pérez-Moreno’s Group concentrates on the
role of cell adhesion, inflammation and cellular signalling in
normal skin physiology and cancer development, whereas Nabil
Djouder’s Group aims to dissect the contribution of nutrient
and growth factor signalling pathways to cancer development.
Massimo Squatrito’s Group – in part supported by the Seve
Ballesteros Foundation ( F-SB ) – studies how brain tumours,
mainly glioblastomas and medulloblastomas, develop and how
they respond to therapy. The Senior Group, led by Francisco X.
Real, studies epithelial tumours focussing on pancreatic and
bladder cancer. The Group employs an integrative approach to
understand the molecular patho-physiology of these tumours
and to apply this knowledge to the clinical setting.
SCIENTIFIC REPORT 2014 52 SPANISH NATIONAL CANCER RESEARCH CENTRE, CNIO 53Vice-Direction of Basic Research BBVA Foundation-CNIO Cancer Cell Biology Programme | Genes, Development and Disease Group
GENES, DEVELOPMENT Erwin F. Wagner
Group Leader
Staff Scientists
Latifa Bakiri, Nuria Gago (Since July),
Post-Doctoral Fellows
Albanderi Alfraidi (Since September),
Graduate Students
Lucía T. Díez (Since September),
Technicians
Vanessa Bermeo, Ana Guio, Jakob
AND DISEASE GROUP Juan Guinea-Viniegra (Until July),
María Jiménez, Helia B. Schönthaler
Rainer W. Hamacher, Michele
Petruzzelli (Until July), Álvaro Ucero
Stefanie Wurm Schnabl (March-September),
Stephania Tocci (Since October)
(Until April), Özge Uluçkan
OVERVIEW
Our studies aim to analyse gene function in healthy and “ We aim to make CNIO a more
pathological conditions, e.g. in tumour development, using international institution. At
the mouse as a model organism, but also employing patient-
present 4 out of 5 Group Leaders
derived samples. Specifically the functions of the AP-1 ( Fos/
Jun ) transcription factor complex regulating cell proliferation,
in our department are foreigners ;
differentiation and oncogenesis, as well as the cross-talk between 1 is partly funded by the Seve
organs are being investigated. The ultimate goal is to define Ballesteros Foundation. Fifteen
molecular pathways leading to disease development and to different nationalities ensure an
identify novel therapeutic targets. We focus on : international science culture and all
focus on unravelling the mysteries of
ɗɗ Elucidating a causal link between inflammation, cancer and cancer.”
AP-1 ( Fos/Jun ) expression, using cell type-specific, switchable
genetically engineered mouse models ( GEMMs ).
ɗɗ Developing and characterising new GEMMs for cancer and
human diseases, such as bone loss, fibrosis and psoriasis, and
apply these to preclinical studies.
ɗɗ Using large-scale genomic or proteomic approaches to
compare mouse models of disease to human disease and
identify therapeutically relevant targets.
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS
We have developed a powerful technology for switchable, Liver disease – inflammation, metabolism, fibrosis and
reversible and tissue-specific ectopic gene expression of specific cancer
AP-1 monomers/dimers in the liver, skin and bone. We use
mouse and human tissue samples for large-scale studies, such as In hepatitis, c-Jun is a mediator of cell survival specifically
deep sequencing ( RNA-Seq, ChIP-Seq ) and mass spectrometry in hepatocytes, while the absence of JunB in immune cells is
analyses. beneficial. Mechanistically, JunB promotes cell death during
acute hepatitis by regulating interferon-γ production, thus
functionally antagonising the hepato-protective function of c-Jun.
Bone development and sarcomas
Fra-1/2 proteins appear to be dispensable for liver fibrosis, while
We are studying the function of Fos proteins and their targets they are important novel modulators of hepatic lipid metabolism.
such as TGFBI using loss- and gain-of-function mouse models. AP-1 modulates hepatic lipid storage and steatosis formation by
We found that Fos protects osteoblasts from replicative stress controlling PPARγ transcription. Strikingly, AP-1 dimers can either
and DNA damage through Chk1 upregulation ; a mechanism that induce or repress PPARγ expression. Therefore, fatty liver disease
is most likely relevant to osteosarcoma development. and obesity most likely depend on the composition of AP-1 dimers.
SCIENTIFIC REPORT 2014 54 SPANISH NATIONAL CANCER RESEARCH CENTRE, CNIO 55VICE-DIRECTION OF BASIC RESEARCH BBVA FOUNDATION-CNIO CANCER CELL BIOLOGy PROGRAMME | GENES, dEvELOPmENT ANd dISEASE GROuP
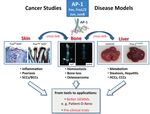
Figure 1 Tet-switchable AP-1 trans- AP-1-dependent inflammation and skin hyperplasia Role of S100A8/A9 and complement C3 in psoriasis Figure 2 Defining AP-1( Fos/Jun ) func-
genic mice were generated for ectopic tions in skin/epidermis. On the left side,
c-Fos mmp10 / s100a7a15
expression of specific AP-1 monomers/ TIMP3
S100A8/A9 the functions of the AP-1 proteins c-Fos,
dimers in the liver, skin and bone. Pro- TACE
Fra-2 and JunB in skin inflammation,
Keratinocyte
TNFa
teomics, expression profiling, RNA-se- S100A8/A9 NFkB barrier function and the link to bone
quencing and ChIP-sequencing are C3
loss are depicted. On the right side, a
CD4 T cell recruitment CFB
employed to compare mouse models DAMP-
receptors
newly discovered pathway with novel
of disease to human disease and to CCL2 C3b/CFB C3a
targets for psoriasis is described.
IL-22
identify novel targets. Preclinical studies Cytokine signaling
RANTES
and others
are performed in our AP-1-dependent Complement C3
mouse models with compounds that Epidermal proliferation, survival
C3R/ IL-1R
CD11b DAMP-
receptors
target the identified molecules to deter- Hyperplastic lesions - SCC (+DMBA)
mine the potential of translating our Briso E. et al., G&D, 2013
Schonthaler H. et al., Immunity, 2013
findings for treating human disease.
Fra-2 links barrier function to inflammation Skin Role of miR-21 and TIMP-3 in psoriasis
WT Fra-2Δep
Epidermis Non-lesional Lesional
JunB/AP-1
IL-6
JunB/p-Stat3 p-Stat3
Non-lesional Lesional
JunB links skin inflammation to bone loss miRNA-21
WT JunBΔep
TIMP-3
TACE
miRNA21
Non-lesional Lesional
Psoriasis
TIMP-3
Ectopic c-Fos expression and its dimers lead to spontaneous liver providing a promising new target to prevent/delay cachexia in Skin cancer, inflammation and human disease the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines that affect the
inflammation, fibrosis, hepatocyte/bile duct hyperproliferation cancer patients. differentiation of bone-forming osteoblasts. We extended our
and cancer. Deletion of c-Fos in hepatocytes protects from Since we found increased c-Fos expression in Squamous Cell studies to psoriasis patients and have shown that they have
chemically-induced liver carcinogenesis, whereas deletion in Carcinomas ( SCCs ), we modelled SCC development in mice bone loss.
immune cells abrogates this protective effect. A function for AP-1 in the lung with inducible c-Fos expression. We identified an essential role of
c-Fos in modulating immune cell recruitment to the skin, which New approaches including genetic and biochemical analyses by
We have recently documented the connection between the contributes to skin cancer development. We also demonstrated proteomics of mouse and human skin samples were performed ;
Role of white adipose tissue in cancer-associated Fos protein Fra-1 and major transcription factors controlling that loss of epidermal Fra-2 protein results in skin barrier defects. these unravelled novel pathways and molecules for targeted
cachexia epithelial to mesenchymal transition ; a process crucial to Mechanistically, Fra-2 binds and transcriptionally regulates therapies, such as S100A8/A9 and complement C3 ( FIGURE
epithelial cancers. The contribution of Fra1/2 proteins to lung epidermal differentiation gene promoters, which are co-occupied 2 ). In addition, a potential role of specific miRNAs, e.g. miR21
Various cancer mouse models were employed to discover a fibrosis and cancer is currently being studied using GEMMs, as by the transcriptional repressor Ezh2. involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis was established.
consistent metabolic and phenotypic switch from white to brown well as lung cancer samples from patients. This study is conducted Human skin samples are provided by our collaborator Esteban
fat ( browning ) in cachectic mice. The role of browning as a in collaboration with Mariano Barbacid’s Experimental Oncology Characterisation of the epidermal inflammatory disease in mice Daudén from Hospital Universitario de La Princesa ( Madrid,
contributor to the wasting process was further characterised, Group at the CNIO and the Daiichi Sankyo Company in Japan. lacking JunB suggests a skin to bone cross-talk. JunB represses Spain ). s
∞ PUBLICATIONS ∞∞ Petruzzelli M, Schweiger M, Schreiber Fillatreau S, Berberich I, Hobeika E, Reth liver fibrosis, but modulates xenobiotic ly member widely expressed in cancer. adipocyte differentiation and survival by S, Bauer C, Schorpp-Kistner M, Hess J, thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension.
R, Campos-Olivas R, Tsoli M, Allen J, M, Wagner EF, Schett G, Mielenz D, David metabolism. Hepatology 59, 261-273. Oncogene 33, 2513-2519. regulating PPARg and hypoxia. Cell Death Holland-Cunz S, Wagner EF, Eils R, Angel Arterioscl Throm Vas 34, 810-819.
∞∞ Tummala KS, Gomes AL, Yilmaz, Graña Swarbrick M, Rose-John S, Rincon M, JP ( 2014 ). The AP-1 transcription factor ∞∞ Hefetz-Sela S, Stein I, Klieger Y, Porat ∞∞ Bakiri L, Macho-Maschler S, Custic I, Nie- Differ 21, 655-664. P, Hartenstein B ( 2014 ). Efficient Kerat- ∞∞ Bakiri L, Hasenfuss SC, Wagner EF ( 2014 ).
O, Bakiri L, Ruppen I, Ximénez-Embún P, Robertson G, Zechner R, Wagner EF Fra1 inhibits follicular B cell differentiation R, Sade-Feldman M, Zreik F, Nagler A, miec J, Guío-Carrión A, Hasenfuss SC, Eger ∞∞ Thomsen MK, Bakiri L, Hasenfuss SC, Wu inocyte Differentiation Strictly Depends A FATal AP-1 dimer switch in hepatostea-
Sheshappanavar V, Rodriguez-Justo M, ( 2014 ). A switch from white to brown into plasma cells. J Exp Med 211, 2199-2212. Pappo O, Quagliata L, Dazert E, Eferl R, A, Müller M, Beug H, Wagner EF. Fra-1/AP-1 H, Morente M, Wagner EF. Loss of JUNB/ on JNK-Induced Soluble Factors in Fibro- tosis. Cell Cycle 13, 1218-1219.
Pisano DG, Wagner EF, Djouder N ( 2014 ). fat increases energy expenditure in ∞∞ Wurm S, Zhang J, Guinea-Viniegra J,Garcia Terracciano L, Wagner EF, Ben-Neriah Y, induces EMT in mammary epithelial cells AP-1 promotes invasive prostate cancer. blasts. J Invest Dermatol 134, 1332-1341. ∞∞ Schulze J, Lopez-Contreras AJ, Uluçkan
Inhibition of De Novo NAD+ Synthesis by cancer-associated cachexia. Cell Metab F, Muñoz J, Bakiri L, Ezhkova E, Wagner Baniyash M, Pikarsky E ( 2014 ). Acquisition by modulating Zeb1/2 and TGFβ expres- Cell Death Differ. PMID : 25526087. ∞∞ Alias S, Redwan B, Panzenböck A, Win- O, Graña-Castro O, Fernandez-Capetillo
Oncogenic URI Causes Liver Tumorigen- 20, 433-447. EF. Terminal epidermal differentiation of an immunosuppressive protumorigenic sion. Cell Death Differ. PMID : 25301070. ∞∞ Glitzner E, Korosec A, Brunner PM, Drobits ter MP, Schubert U, Voswinckel R, Frey O, Wagner EF ( 2014 ). Fos-dependent in-
esis through DNA Damage. Cancer Cell ∞∞ Guinea-Viniegra J, Jiménez M, Schonthaler is regulated by the interaction of Fra-2/ macrophage phenotype depending on ∞∞ Galluzzi L et al. ( incl. Wagner EF ). Essen- B, Amberg N, Schonthaler HB, Kopp T, MK, Jakowitsch J, Alimohammadi A, duction of Chk1 protects osteoblasts from
26, 826-839. HB, Navarro R, Delgado Y, Concha-Garzón AP-1 with Ezh2 and ERK1/2. Genes Dev. c-Jun phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad tial versus accessory aspects of cell death : Wagner EF, Stingl G, Holcmann M, Sibilia Hobohm L, Mangold A, Bergmeister H, replication stress. Cell Cycle 13, 1980-1986.
∞∞ Hasenfuss SC, Bakiri L, Thomsen MK, Wil- MJ, Tschachler E, Obad S, Daudén E, Wag- PMID : 25547114. Sci USA 111, 17582-17587. recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell M ( 2014 ). Specific roles for dendritic cell Sibilia M, Wagner EF, Mayer E, Klepetko
liams EG, Auwerx J, Wagner EF ( 2014 ). ner EF ( 2014 ). Targeting miR-21 to treat ∞∞ Hasenfuss SC, Bakiri L, Thomsen MK, Ha- ∞∞ Palla AR, Piazzolla D, Abad M, Li H, Death Differ. PMID : 25236395. subsets during initiation and progression W, Hölzenbein TJ, Preissner KT, Lang IM
Regulation of steatohepatitis and PPARg psoriasis. Sci Transl Med 6, 225re1. macher R, Wagner EF ( 2014 ). Activator Dominguez O, Schonthaler HB, Wagner ∞∞ Luther J, Ubieta K, Hannemann N, Jimenez of psoriasis. EMBO Mol Med 6, 1312-1327. ( 2014 ). Defective angiogenesis delays
signaling by distinct AP-1 dimers. Cell ∞∞ Grötsch B, Brachs S, Lang C, Luther J, protein 1 transcription factor fos-related EF, Serrano M ( 2014 ). Reprogramming M, Garcia M, Zech C, Schett G, Wagner ∞∞ Schumacher M, Schuster C, Rogon ZM, thrombus resolution : a potential patho-
Metab 19, 84-95. Derer A, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U, Bozec A, antigen 1 ( fra-1 ) is dispensable for murine activity of NANOGP8, a NANOG fami- EF, Bozec A ( 2014 ). Fra-2/AP-1 controls Bauer T, Caushaj N, Baars S, Szabowski genetic mechanism underlying chronic
SCIENTIFIC REPORT 2014 56 SPANISH NATIONAL CANCER RESEARCH CENTRE, CNIO 57Vice-Direction of Basic Research BBVA Foundation-CNIO Cancer Cell Biology Programme | Epithelial Carcinogenesis Group
EPITHELIAL Francisco X. Real
Group Leader
Staff Scientists
Arancha Cebrián (Until February),
Post-Doctoral Fellows
Enrique Carrillo, Luis C. Fernández,
Graduate Students
Cristina Balbás (Until July), Isidoro
Technicians
Inmaculada Almenara (February-
CARCINOGENESIS GROUP M. Teresa Gómez Del Pulgar (Until
February), Paola Martinelli (Until
Eleonora Lapi, Miriam Marqués Cobo, Francesc Madriles, Catarina
Pereira (Since November), Laia
October), Natalia Del Pozo, Carme
Társila Guerrero (April-September),
September), Victor J. Sánchez- Richart María Tania Lobato, Ana Sagrera
Arevalo
contribution of these cell types to PDAC is crucial to design better “ Our work has highlighted novel
strategies for early tumour detection and prevention in subjects at aspects of the role of transcription
risk. Regarding urothelial cell carcinoma ( UCC ), we are interested factors involved in acinar
in identifying new genes that can then be used for improved
differentiation ( i.e. GATA6, HNF1A )
tumour taxonomy, characterising the mechanisms through
which they participate in cancer, and apply this knowledge for
as important players in PDAC ; we
improved prediction of outcome and therapy. have shown that the MNK1 kinase
is key to the stress response in
acinar cells. Furthermore, we have
characterised new aspects of the
molecular genetics of bladder
cancer.”
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS
Pancreas cancer molecular pathophysiology the secretory response ( FIGURE 1 ). We are currently evaluating
its role in mutant KRas-driven PDAC using mouse models. This
Cell differentiation as a tumour suppressor mechanism in the work benefits from a close collaboration with the other groups
pancreas. PDAC is characterised by highly prevalent alterations in working on PDAC at the CNIO ( Marinano Barbacid from the
KRAS, p16, TP53, and SMAD4 and by low-frequency alterations Experimental Oncology Group ; Christopher Heeschen from
in a plethora of other genes converging in a few critical genetic the Stem Cells and Cancer Group ; Manuel Hidalgo from the
pathways. Our main interest is to identify new players involved Gastrointestinal Cancer Clinical Research Unit ; and Núria
in the early steps of tumour development. We have acquired Malats from the Genetic and Molecular Epidemiology Group ).
evidence that transcription factors involved in the fine-tuning
of acinar cell differentiation ( i.e. Gata6, Hnf1a, and Nr5a2 )
also play an important role. Gata6 inactivation in pancreatic Urothelial cell carcinoma ( UCC ) genetics and biology
progenitors accelerates KRas-driven PDAC progression in mice
and GATA6 is deleted in a subset of human PDAC, supporting Our goal is to refine current knowledge on the genomic landscape
its role as a tumour suppressor. GATA6 controls the epithelial- of UCC and to apply this in the clinical setting. Hotspot TERT
OVERVIEW mesenchymal transition and also regulates a “ basal signature ” promoter mutations are the most common genetic change in
in PDAC that is shared with breast and bladder tumours. UCC and occur early on during tumour progression. TERT
Other genes that participate in development, differentiation, mutant tumours do not display higher levels of TERT mRNA
We focus on the molecular/cellular mechanisms involved in be made at either of these levels and can then be extended through pancreatitis, and PDAC include Nr5a2, Hnf1a, Foxa1/2, and than wild type counterparts, pointing to the notion that they may
pancreatic and bladder cancer with a disease-oriented approach. additional work. Myc. RNA-Seq and ChIP-Seq experiments have enabled us act through mechanisms other than increased transcriptional
Our strategy resembles a pyramid having as base an equilateral to identify intricate relationships between them through activity. Intriguingly, TERT mutations are not associated with
triangle. The 3 vertexes correspond to the used models : patient In regards to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma ( PDAC ), we are regulatory networks controlling tumour suppressors, epigenetic genetic or environmental risk factors for UCC and they are
samples, cell cultures, and genetically modified mice. The third interested in the early events involved in tumour development regulation, metabolic processes, and inflammatory cytokine promising candidates for non-invasive tumour detection in
dimension comes from the projection of this knowledge to the with a particular focus on cell differentiation as a critical tumour cascades. Factors supporting acinar cell differentiation also exfoliated cells in urine.
“ population ” level : we bring the biology to large-scale studies suppressor mechanism. These processes cannot be readily studied repress – directly or indirectly – inflammatory genes. Among
with patients. We are interested in the genetic susceptibility to using human samples. Therefore, we use the excellent genetic the signalling components, we have identified the stress kinase Through exome sequencing we have identified new genes and
cancer and in developing better molecular tools to predict patient mouse models that are available to us. PDAC can originate both in Mnk1 that is selectively expressed at high levels in acinar cells, pathways involved in UCC and we are focusing on STAG2, a
outcomes or response to therapy. Our primary observations can pancreatic progenitors and in acinar cells. The elucidation of the is regulated during pancreatitis and cancer, and is required for cohesin component. STAG2 inactivation is more frequent in non
SCIENTIFIC REPORT 2014 58 SPANISH NATIONAL CANCER RESEARCH CENTRE, CNIO 59Vice-Direction of Basic Research BBVA Foundation-CNIO Cancer Cell Biology Programme | Epithelial Carcinogenesis Group
Figure 1 Mnk1 is an acinar-specific muscle-invasive tumours and is not associated with aneuploidy, specific therapeutic sensitivities ( FIGURE 2 ). We are exploring
stress kinase required for cell prolif-
eration upon pancreatic damage and suggesting that STAG2 participates in UCC through mechanisms whether “ luminal ”, “ basal ”, and “ inflammatory ” signatures are
for optimal exocrine secretion. (A) different from those involved in chromosome segregation. We associated with clinical/pathological features and with patient
Mnk1 expression in mouse pancreas. are generating conditional Stag2-null mice to study how Stag2 outcomes. This information will be integrated with germline
(B) c-Myc and Ccnd1 levels in WT and
KO pancreata upon acute pancreatitis inactivation contributes to urothelial tumour development/ and somatic genomic analyses and will be used for the design
(n=4). (C) Caerulein-induced amylase progression. of clinical trials in collaboration with the SOGUG ( Spanish
release by isolated WT and KO acini. (D) Oncology Genitourinary Group ) cooperative group.
MRCP images showing secretin-induced
fluid secretion into the duodenum of In the last few years, a new molecular taxonomy of UCC with
WT and KO mice. broad clinical implications is emerging. Using genetic mouse This work is being conducted in close collaboration with Núria
models we have shown that the concurrent inactivation of Malats’ Group at the CNIO, with SOGUG, and with a European
Pten and Tp53 in the urothelium leads to carcino-sarcomatoid Consortium of collaborators. s
tumours, which is in line with this taxonomy, and demonstrates
∞∞ PUBLICATIONS creatitis in a European replication study. tinelli P, Hübner N, Stanton LW, Real FX, Blanco-Aparicio C, García Collazo AM,
Gut. PMID : 25253127. Bourillot PY, Savatier P ( 2014 ). Klf4 and Cantalapiedra EG, Fernández JP, Curiel
∞∞ Wolpin BM et al. ( incl. Malats N, Real ∞∞ Flandez M, Cendrowski J, Cañamero M, Klf5 differentially inhibit mesoderm and del Olmo S, Pisonero H, Madureira R, Al-
FX ) ( 2014 ). Genome-wide association Salas A, Del Pozo N, Schoonjans K, Real FX endoderm differentiation in embryonic maraz C, Mollejo M, Alves FJ, Menárguez
study identifies multiple susceptibility ( 2014 ). Nr5a2 heterozygosity sensitises stem cells. Nat Commun 5, 3719. J, González-Palacios F, Rodríguez-Peralto
loci for pancreatic cancer. Nat Genet 46, to, and cooperates with, inflammation in ∞∞ Hoskins JW, Jia J, Flandez M, Parikh H, JL, Ortiz-Romero PL, Real FX, García JF,
994-1000. KRasG12V-driven pancreatic tumourigen- Xiao W, Collins I, Emmanuel MA, Ibrahim Bischoff JR, Piris MA ( 2014 ). PIM kinases
∞∞ Whissell G, Montagni E *, Martinelli P *, Her- esis. Gut 63, 647-655. A, Powell J, Zhang L, Malets N, Bamlet WR, as potential therapeutic targets in a subset
nando-Momblona X, Sevillano M, Jung ∞∞ Maraver M, Fernandez-Marcos PJ, Cash Peterson GM, Real FX, Amundadottir LT of peripheral T cell lymphoma cases. PLoS
P, Cortina C, Calon A, Abuli A, Castells TP, Mendez-Pertuz M, Dueñas M, Maietta ( 2014 ). Transcriptome analysis of pan- One 9, e1121148.
A, Castellvi-Bel S, Nacht AS, Sancho E, P, Martinelli P, Muñoz-Martin M, Martín- creatic cancer reveals a tumor suppressor ∞∞ Pineda S, Milne RL, Calle ML, Rothman N,
Stephan-Otto Attolini C, Vicent GP, Real ez-Fernández M, Cañamero M, Roncador function for HNF1A. Carcinogenesis 35, López de Maturana E, Herranz J, Kogevi-
FX, Batlle E (2014). The transcription factor G, Martinez-Torrecuadrada JL, Grivas D, de 2670-2678. nas M, Chanock SJ, Tardón A, Márquez M,
GATA6 enables self-renewal of colon ade- la Pompa JL, Valencia JL, Paramio JM, Real ∞∞ Salas LA, Villanueva CM, Tajuddin SM, Guey LT, García-Closas M, Lloreta J, Baum
noma stem cells by repressing BMP gene FX, Serrano M. Notch pathway inactivation Amaral AF, Fernandez AF, Moore LE, Car- E, González-Neira A, Carrato A, Navarro
expression. Nat Cell Biol 16, 695-707. *These promotes bladder cancer progression. J rato A, Tardón A, Serra C, García-Closas A, Silverman DT, Real FX, Malats N ( 2014 ).
authors contributed equally to this work. Clin Invest. PMID : 25574842. R, Basagaña X, Rothman N, Silverman DT, Genetic Variation in the TP53 Pathway and
∞∞ Barceló C, Etchin J, Mansour MR, Sanda ∞∞ Allory Y, Beukers W, Sagrera A, Flandez Cantor KP, Kogevinas M, Real FX, Fraga Bladder Cancer Risk. A Comprehensive
T, Ginesta MM, Sanchez-Arévalo Lobo VJ, M, Marques M, Marquez M, van der Keur MF, Malats N ( 2014 ). LINE-1 methylation Analysis. PLoS One 9, e89952.
Figure 2 Adeno-Cre-mediated dele- Real FX, Capellà G, Estanyol JM, Jaumot A, Dyrskjot L, Lurkin I, Vermej M, Carrato in granulocyte DNA and trihalomethane ∞∞ Vedder MM, Márquez M, de Bekker-Grob
tion of Pten and p53 in the bladder M, Look AT, Agell N ( 2014 ). Ribonucleo- A, Lloreta J, Lorente JA, Carrillo-de-San- exposure is associated with bladder can- EW, Calle ML, Dyrskjøt L, Kogevinas M,
epithelium leads to the development protein HNRNPA2B1 interacts with and ta-Pau E, Masius RG, Kogevinas M, Steyer- cer risk. Epigenetics 9, 1532-1539. Segersten U, Malmström PU, Algaba F,
of highly aggressive carcino-sarcoma- regulates oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic berg EW, van Tilborg AAG, Abas C, Orntoft ∞∞ Tajuddin SM, Amaral AF, Fernández AF, Beukers W, Orntoft TF, Zwarthoff E, Real
toid tumours (A), expressing smooth ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Gastroen- TF, Zuiverloon TCM, Malats N, Zwarthoff Chanock S, Silverman DT, Tardón A, Carra- FX, Malats N, Steyerberg EW ( 2014 ). Risk
muscle actin (B), KRT5 (C) and KRT14 terology 147, 882-892. EC, Real FX ( 2014 ). Telomerase reverse to A, García-Closas M, Jackson BP, Toraño prediction scores for recurrence and pro-
(D). According to the recent taxonom- ∞∞ Hermann PC, Sancho P, Cañamero M, transcriptase promoter mutations in blad- EG, Márquez M, Urdinguio RG, García-Clo- gression of non-muscle invasive bladder
ical classifications, these features are Martinelli P, Madriles F, Michl P, Gress T, der cancer : high frequency across stages, sas R, Rothman N, Kogevinas M, Real FX1, cancer : an international validation in
typical of “genomically unstable” and de Pascual R, Gandia L, Guerra C, Barbacid detection in urine, and lack of association Fraga MF, Malats N ; Spanish Bladder Can- primary tumours. PLoS One 9, e96849.
“p53-like”-type human tumours. M, Wagner M, Vieira CR, Aicher A, Real with outcome. Eur Urol 65, 360-366. cer/EPICURO Study investigators. ( 2014 ). ∞∞ de Maturana EL, Chanok SJ, Picornell
FX, Sainz B Jr, Heeschen C ( 2014 ). Nico- ∞∞ Gerlinger M, Catto JW, Orntoft TF, Real LINE-1 methylation in leukocyte DNA, in- AC, Rothman N, Herranz J, Calle ML,
tine Promotes Initiation and Progression FX, Zwarthoff EC, Swanton C. Intratumour teraction with phosphatidylethanolamine García-Closas M, Marenne G, Brand A,
of KRAS-Induced Pancreatic Cancer via Heterogeneity in Urologic Cancers : From N-methyltransferase variants and bladder Tardón A, Carrato A, Silverman DT, Ko-
Gata6-Dependent Dedifferentiation of Molecular Evidence to Clinical Implica- cancer risk. Br J Cancer 110, 2123-2130. gevinas M, Gianola D, Real FX, Malats
Acinar Cells in Mice. Gastroenterology tions. Eur Urol. PMID : 24836153. ∞∞ Dueñas M, Martínez-Fernández M, N ( 2014 ). Whole genome prediction of
147, 1119-1133. ∞∞ Masson-Lecomte A, Rava M, Real FX, García-Escudero R, Villacampa F, Marqués bladder cancer risk with the Bayesian
∞∞ Cendrowski J, Sánchez-Arévalo Lobo VJ, Hartmann A, Allory Y, Malats N ( 2014 ). M, Saiz-Ladera C, Duarte J, Martínez V, LASSO. Genet Epidemiol 38, 467-476.
Sendler M, Salas A, Kühn JP, Molero X, Inflammatory Biomarkers and Bladder Gómez MJ, Martín ML, Fernández M, Cas-
Fukunaga R, Mayerle J, Lerch MM, Real Cancer Prognosis : A Systematic Review. tellano D, Real FX, Rodriguez-Peralto JL, ∞∞ AWARDS AND RECOGNITION
FX. Mnk1 is a novel acinar cell-specific Eur Urol 66, 1078-1091. De La Rosa F, Paramio JM. PIK3CA gene
kinase required for exocrine pancreatic ∞∞ Real FX, Boutros PC, Malats N ( 2014 ). alterations in bladder cancer are frequent ∞∞ Associate Editor, Bladder.
secretion and response to pancreatitis Next-generation Sequencing of Urologic and associate with reduced recurrence in ∞∞ Associate Editor, Bladder Cancer.
in mice. Gut. PMID : 25037190. Cancers : Next Is Now. Eur Urol 66, 4-7. non-muscle invasive tumors. Mol Carcin- ∞∞ European Pancreatic Club Council Pres-
∞∞ Derikx MH et al. ( incl. Malats N, Real ∞∞ Aksoy I, Giudice V, Delahaye E, Wianny F, ogen. PMID : 24347284. ident ( 2015 ).
FX ). Polymorphisms at PRSS1-PRSS2 Aubry M, Mure M, Chen J, Jauch R, Bogu ∞∞ Martín-Sánchez E, Odqvist L,
and CLDN2-MORC4 loci associate with GK, Nolden T, Himmelbauer H, Xavier Doss Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Sánchez-Beato
alcoholic and non-alcoholic chronic pan- M, Sachinidis A, Schulz H, Hummel O, Mar- M, Roncador G, Domínguez-González B,
SCIENTIFIC REPORT 2014 60 SPANISH NATIONAL CANCER RESEARCH CENTRE, CNIO 61Vice-Direction of Basic Research BBVA Foundation-CNIO Cancer Cell Biology Programme | Epithelial Cell Biology Junior Group
EPITHELIAL CELL BIOLOGY Mirna Pérez-Moreno
Junior Group Leader
Graduate Students
Ljiljana Dukanovic,
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS
JUNIOR GROUP Post-Doctoral Fellow
Marta N. Shahbazi (until June)
Donatello Castellana Technician Mechanisms regulating epidermal progenitor cells ’ cell behaviour, such as proliferation, survival and migration,
Francesca Antonucci
self-renewal and differentiation are less understood.
One of the fundamental questions in the biology of tissues We have uncovered a mechanism by which epidermal progenitor
is how they acquire an adequate control of cell division and cells sense injury and promote repair of epithelial layers. This
differentiation. We continue exploring the role of novel players, involves the adherens junctions protein p120-catenin, whose
including mitotic and cytoskeletal proteins, in the regulation role extends beyond intercellular adhesion to the regulation
of epidermal progenitor’s self-renewal through oriented cell of inflammatory responses and epithelial remodelling upon
divisions, using mouse epidermal development as a model tissue injury, as well as being potentially implicated in chronic
system. In addition, we are investigating how these novel players inflammation and cancer.
may be involved in regulating proper epidermal differentiation,
tissue architecture and barrier function. We believe these Moreover, we have identified a novel connection between
results may spawn new concepts about how these molecules skin progenitor cells and macrophages that modulates their
regulate tissue homeostasis and how, when disrupted, they regenerative potential. Under physiological conditions, in non-
lead to disease. inflamed, non-transformed skin, a subset of skin macrophages
surround hair follicle stem cells (Vice-Direction of Basic Research BBVA Foundation-CNIO Cancer Cell Biology Programme | Growth Factors, Nutrients and Cancer Junior Group
GROWTH FACTORS, Nabil Djouder
Junior Group Leader
Post-Doctoral Fellows
Hugo Bernard, Stefan Burén (until
Graduate Students
Marta Brandt, Almudena Chaves,
NUTRIENTS AND CANCER September), Mohamad-Ali Fawal,
Ana Gomes
Ana Teijeiro, Krishna Seshu Tummala
JUNIOR GROUP
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS
Figure Milestones in URI research at the CNIO: scheme illus-
trating present and future research at CNIO, involving a better
understanding of the growth factor and nutrient circuitries
implicated in liver, intestine/colon and pancreas disorders.
Our laboratory studies the molecular mechanisms of diseases Genetically engineered mouse models
associated to dysregulations in growth factor and nutrient
signalling cascades. We have a particular interest in metabolic We identified new components of the growth factors and nutrients
organs such as the liver, intestine and pancreas, as these 3 organs signalling cascades. Mouse models were generated in our lab
are physiologically interconnected and influenced through in order to study their impact on liver, pancreas and intestinal
their exocrine and/or endocrine functions. Identifying new diseases. Elucidating molecular mechanisms will offer strategic
components of growth factor and nutrient circuitries, as well as therapeutic interventions to prevent and cure human diseases. s
OVERVIEW elucidating their role and functions in vivo by generating new
mouse models, will help us to better understand how growth
factors and nutrients impact on the patho-physiological state
As Western society has shifted to a higher caloric diet with nutrients “ Developing new mouse models that of metabolic disorders and cancer.
overload and a more sedentary lifestyle, the incidence of metabolic mimic different stages of human
syndrome and cancer has increased to epidemic proportions.
diseases, and the identification and
Using mouse models combined with biochemical techniques, our Identifying new components of growth factor and
laboratory is interested in delineating the growth factor and nutrient
validation of gatekeeper pathways in nutrient circuits
signalling cascades that impact on the patho-physiolological states early disease stages may offer new ∞∞ PUBLICATION esis through DNA Damage. Cancer Cell
of metabolic diseases and cancer. Successful outcomes in new therapeutic strategies to prevent To decipher the growth factor and nutrient signalling cascades, ∞∞ Tummala KS, Gomes AL, Yilmaz M, Graña
26, 826-839.
mechanistic insights of circuits associated to growth factors and and cure metabolic dysfunctions and in addition to biochemical approaches, we screened for new O, Bakiri L, Ruppen I, Ximénez Embún P, ∞∞ PATENT
nutrients may improve the predictive clinical potential and should cancer.” components of the growth factors and nutrients cascade using Sheshappanavar V, Rodriguez-Justo M,
Pisano D, Wagner EF, Djouder N ( 2014 ). Djouder N, Tummala KS ( 2104 ). Methods
facilitate development of innovative mechanism-based therapeutics live-cell imaging based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer
∞∞
Inhibition of De Novo NAD+ Synthesis by for Treating Cancer. EP14382298.9.
to treat metabolic dysfunctions and cancer. ( FRET ). Oncogenic URI Causes Liver Tumorigen-
SCIENTIFIC REPORT 2014 64 SPANISH NATIONAL CANCER RESEARCH CENTRE, CNIO 65Vice-Direction of Basic Research BBVA Foundation-CNIO Cancer Cell Biology Programme | Seve Ballesteros Foundation-CNIO Brain Tumour Junior Group
SEVE BALLESTEROS Massimo Squatrito
Junior Group Leader
Graduate Students
Carolina Almeida,
OVERVIEW
FOUNDATION-CNIO BRAIN Staff Scientists
Alvaro Curiel (since February)
TUMOUR JUNIOR GROUP Bárbara Oldrini, Alberto J.
Schuhmacher
Technician
Claudia S. Troncone (since August)
Malignant gliomas ( astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas and
oligoastrocytomas ) are the most frequent forms of brain tumour,
ineffective; this is largely due to its intrinsic resistance to the current
therapeutic modalities and its high cellular heterogeneity.
of which Glioblastoma Multiforme ( GBM ), classified as grade IV
astrocytoma, is the most lethal tumour of the central nervous system In our laboratory we use a combination of genomic analyses,
in adults. Standard treatment for GBM consists of surgical resection mouse models and primary tumour cell cultures, with the ultimate
of the tumour and postoperative treatment with chemotherapy goal of identifying the molecular mechanisms that could provide
and ionising radiation. Despite advances in surgical and imaging the basis for the development of novel treatments for GBM
techniques, the treatments that are available for GBM are still patients.
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS
New imaging tools for GBM tumours with an alkylating agent known as Temozolomide ( TMZ ). The
most frequent resistance mechanism to TMZ treatment is
Positron Emission Tomography ( PET ) is an imaging modality that the expression of the DNA-repair gene, O 6-methylguanine-
is widely used in oncology for staging, monitoring the efficacy of DNA-methyltransferase ( MGMT ), although other resistance
a given treatment, and to follow-up tumour recurrence ; it offers mechanisms still have to be identified. In collaboration with the
an in vivo quantitative and functional evaluation at the molecular CNIO Genomic Instability Group, we are conducting genetic
level. 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose ( 18F-FDG ) is the most frequently screenings in haploid human cells in order to identify novel
used radiopharmaceutical in clinical imaging. 18F-FDG, however, modulators of TMZ sensitivity. s
has limited usefulness in brain tumours, such as GBM, due to
the high uptake of glucose by the brain, which causes the image
to have a low signal/background ratio thereby hindering the
identification of the signal from the tumour. Immuno-Positron
Emission Tomography ( immunoPET ) is a novel and attractive
option to improve diagnostic imaging as it combines the high
resolution and quantitative capabilities of PET, with the specificity
and selectivity of monoclonal antibodies ( mAb ) against a given
tumour cell surface marker.
In collaboration with Francisca Mulero ( the Molecular Imaging
Unit ) and Jorge Luis Martínez ( the Proteomics Unit ) from the
CNIO, and other collaborators at the CNIC and CIEMAT, we have
identified a potential novel target for immunoPET imaging GBM.
“ The central focus of our Group is to uncover the genetic MT1-MMP is a membrane-anchored matrix metalloproteinase
whose expression has been shown to be increased with tumour
defects, present in GBM patients, responsible for the
grade in gliomas ; MT1-MMP expression levels in GBM patients
aggressiveness of this tumour type. In particular, we are are associated with worse prognosis. Preliminary studies, using
Figure PET-CT image of a GBM mouse xenograft
performed after injection of a 89Zr-labelled MT1-MMP
interested in the identification of the genetic alterations an antibody vs. MT1-MMP labelled with the positron-emitting antibody.
that lead to the modulation of the activity of the DNA radioisotope 89Zr, have shown promising results regarding the
damage response ( DDR ).” high specificity of such a probe, and suggest multiple potential
clinical applications for this novel imaging tool.
∞∞ PUBLICATIONS ∞∞ Vivanco I, Chen ZC, Tanos B, Oldrini B,
Hsieh WY, Yannuzzi N, Campos C, Melling-
∞∞ Ozawa T, Riester M, Cheng YK, Huse JT, hoff IK. A kinase-independent function of
Therapy resistance mechanisms in GBM Squatrito M, Helmy K, Charles N, Michor F, AKT promotes cancer cell survival. Elife.
Holland EC ( 2014 ). Most human non-GCI- PMID : 25551293.
MP glioblastoma subtypes evolve from a
Standard therapy for GBM includes resection of the tumour common proneural-like precursor glioma.
mass, followed by concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy Cancer Cell 26, 288-300.
SCIENTIFIC REPORT 2014 66 SPANISH NATIONAL CANCER RESEARCH CENTRE, CNIO 67You can also read