Design Challenges for a High-Rate TPC with MPGD Readout - CERN Indico
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
Design Challenges
for a High-Rate TPC
Muon Cooling and Future Muon Facilities
with MPGD Readout
Daniel M. Kaplan
D. M. Kaplan
P. Colas, J. Derré, I. Giomataris
CEA Saclay
Accelerator Physics and Technology Seminar
Fermilab
13TIPP 20112007
February,
Chicago, Illinois
8–14 June 2011Outline
(Varied menu!)
• Antiproton sources
• New antiproton experiments
• Physics goals
• TPC options & challenges
• Summary
D. M. Kaplan, IIT TPC Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 2the Tevatron program (towards the end of 2011 according to the present schedule, although
the possibility of a Tevatron run extension is under consideration). The CERN Antiproton
Antiproton Sources
Decelerator (AD) provides low-energy antiproton beams at a tiny fraction of the intensity
now available at Fermilab. Germany’s ∼ > billion-Euro plan for the Facility for Antiproton
and Ion Research (FAIR) at Darmstadt includes construction — yet to be started — of 30
•
and 90 GeV rapid-cycling
Fermilab synchrotrons
Antiproton and low-isand
Source medium-energy
world’s antiproton storag
most intense
rings [1]. Antiproton operation at FAIR is anticipated on or after 2018.
(and highest-energy)
Table 1: Antiproton energies and intensities at existing and future facilities.
p Stacking: Operation:
Facility Kinetic Energy Rate Duty Hours p/Yr
(GeV) (1010 /hr) Factor /Yr (1013 )
0.005
CERN AD – – 3800 0.4
0.047
Fermilab Accumulator:
Tevatron Collider 8 > 25 90% 5550 > 150
proposed ≈ 3.5–8 20 15% 5550 17
FAIR (∼ > 2018*) 1–14 3.5 15%* 2780* 1.5
...even after FAIR@Darmstadt turns on
∗
The lower number of operating hours at FAIR compared with that at other facilities arises
from the collection ring being shared between the antiproton and radioactive-beam programs.
Due to the modular staging of the FAIR facility, stacking of antiprotons will initially be done
in the experiment ring, leading to the small duty factor shown here. FAIR’s stacking ring is
planned
D. M. Kaplan, IIT for installation several years after initial
TPC operation.
Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 3TAPAS
(The AntiProton Annihilation
Specrometer at Fermilab) Flux Return
Superconducting
solenoid
Our proposal: TOF
TPC
• After Tevatron finishes, SciFi
- Reinstall E760 barrel calorimeter
TOF
}
- Add small magnetic spectrometer
[existing BESS
- Add precision TOF system KEK &
magnet fromi PANDA - Strong interaction studies with antiprotons
MUO
P̅ANDA
FAIR-ESAC/Pbar/Technical Progress Report, January 17, 2005
TOF stop
iii
iv
TOF stop
hadron calorimeter
PANDA - Strong interaction studies with antiprotons
MDC
INFN-Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, Italy
Kungliga Tekniska Högskolan (KTH), Stockholm, Sweden
P. Gianotti, C. Guaraldo, O.N. Hartmann, M. Iliescu, V. Lucherini, E. Pace, C. Petrascu, D. Sirghi,
solenoid B. Cederwall, A. Johnson
F. Sirghi
The PANDA Collaboration Stockholms Universitet, Sweden
o INFN, Sezione di Genova, Italy
22 C. Bargholtz, K. Lindberg, P.E. Tegnér, I. Zartova
R. Ballantini, M. Macri, R. Parodi, A. Pozzo
o Universität Basel, Switzerland DIRC Justus Liebig-Universität Gießen, II. Physikalisches Institut, Germany
Università del Piemonte Orientale Alessandria, Torino and INFN, Sezione di Torino, Italy
140 M. Kotulla, B. Krusche, F. Zehr M.G. Destefanis, W. Döring, P. Drexler, M. Düren, I. Fröhlich, D.G. Kirschner, W. Kühn, K. Makonyi,
M.L. Colantoni, L. Fava, D. Panzieri
coil
Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China V. Metag, M. Nanova, R. Novotny,
dipole
F. Ottone, C. Salz, J. Schneider, B. Seitz, G.-C. Serbanut, Dipartimento di Fisica Generale ’A. Avogadro’, Università di Torino and INFN, Sezione di Torino, Italy
J.J. Xie, B.S. Zou H. Stenzel, U. Thöring M. Thiel M. Alexeev, A. Amoroso, F. Balestra, R. Bertini, M.P. Bussa, O. Denisov, A. Ferrero, L. Ferrero,
RICH V. Frolov, R. Garfagnini, A. Grasso, A. Maggiora, M. Maggiora, G. Pontecorvo, G. Piragino, F. Tosello,
Universität Bochum, I. Institut für Experimentalphysik, Germany University of Glasgow, United Kingdom EMC G. Zosi
EMC
A. Golischewski, K. Götzen, T. Held, H. Koch, EMC B. Kopf, B. Lewandowski, H. Nowak, H. Schmücker, J. Annand,10
o
A. Borissov, D. Ireland, R. Kaiser, J. Kellie, K. Livingston, C. McGeorge, D. Protopopescu,
DIRC M. Steinke, P. Wieczorek, A. Wilms, J. Zhong MDC
G. Rosner Dipartimento di Fisica Generale Università di Torino (a ), Dipartimento di Fisica Sperimentale,
Università di Torino (b ), INFN, Sezione di Torino (c ), IFSI, Sezione di Torino (d ) and Politecnico di
TOF stop
Helmholtz-Institut für Strahlen- und Kernphysik, Bonn, Germany Institut für Kernphysik (a ), Zentralinstitut füror
Elektronik (b ), Forschungszentrum Jülich, Germany
Torino (e ), Italy
EMC STT or TPC
F. Hinterberger M. Drochnerb , W. Gasta , A. Gillitzera , D. Grzonkaa , V. Hejnya , G. Kemmerlingb , H. Kleinesb ,
STT M. Agnelloc,e , E. Bottab,c , T. Bressanib,c , L. Bussoa,c , D. Calvob,c , P. De Remigisc , A. Feliciellob,c ,
beam Università di Brescia, Italy
MDC W. Oelert , D. Prasuhn , J. Ritman , S. Schadmand , A. Sibirtsev , A. Sokolov , T. Stockmanns , F. Ferroc,e , A. Filippib,c , F. Iazzic,e , S. Marcellob,c , G. Mazzac , O. Morrac,d , A. Rivettic , R. Wheadonc
a a a a a a a
MVD H. Ströhera , A. Ucara , P. Vlasova , P. Wintza , P. Wüstnerb
A. Zenoni INFN, Sezione di Trieste and Università di Trieste, Italy
Uniwersytet Slaski, Katowice, Poland
Dipartimento di 0
-1Fisica e Astronomia dell’Università di Catania and1INFN, Sezione di Catania,
2 Italy 3 4 5 6 8 M. Giorgi, A. Martin,
R. Birsa, F.7Bradamante, S. Dalla Torre, 9 P. Schiavon, F. Tessarotto
10
J. Holeczek, J. Kisiel, B. K�los,
M. De Napoli, G. Raciti, E. Rapisarda Physikalisches Institut, Universität Tübingen, Germany
Institute of Modern Physics, the Chinese Academy of Science, Lanzhou, P.R. China
Instytut Fizyki, Uniwersytet Jagiellonski, Cracow, Poland H. Clement, E. Doroshkevitch, K. Ehrhardt, P. Gonser
R. Chen, L. Duan, Z. Hu W. Li, Z. Sun, G. Xiao, Z. Xiao, H. Xu, H. Xu
P. Hawranek, B. Kamys, St. Kistryn, A. Magiera, P. Moskal, B. Piskor-Ignatowicz, The Svedberg Laboratory, Uppsala, Sweden
C. Piskor-Ignatowicz, Z. Rudy, P. Salabura, J. Smyrski, M. Wojciechowski Institut für Kernphysik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz, Germany
H. Calén, C. Ekström, K. Fransson, A. Kupsc, P. Marciniewski
P. Achenbach, J. Pochodzalla, A. Sanchez-Lorente
Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung mbH, Darmstadt, Germany Institutionen för Strålningsvetenskap, Uppsala Universitet, Sweden
U. Lynen, J. Lühning, H. Orth, K. Peters, T.R. Saitoh, C. Schwarz, C. Sfienti Politecnico di Milano (a ), Physics Department, Università di Milano (b ) and INFN, Sezione di
F. Cappellaro, B. Höistad, T. Johansson, I. Lehmann, A. Lundborg, Y.-N. Rao, Ö. Nordhage,
Milano (c ), Italy
Technische Universität Dresden, Germany J. Nyberg, H. Pettersson, K. Schönning, P. Thörngren Engblom, U. Wiedner, J. Zlomanczuk
P. Albertob,c , R. Bassinic , C. Boianoc , I. Iorib,c , S. Riboldia,c
K.-T. Brinkmann, H. Freiesleben, R. Jäkel Universitat de Valencia, Dpto. de Fı́sica Atómica, Molecular y Nuclear, Spain
Research Institute for Nuclear Problems, Belarus State University, Minsk, Belarus
Veksler-Baldin Laboratory of High Energies (VBLHE), Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (a ), J. Diaz
V.I. Dormenev, G.Y. Drobychev, A.A. Fedorov, A.E. Korneev M.V. Korzhik, A.R. Lopatik,
Laboratory of Particle Physics (LPP) (b ), Laboratory of Information Technologies (LIT) (c ), Stefan Meyer Institut für Subatomare Physik, Österreichische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Vienna,
O.V. Missevitch
Laboratory of Nuclear Problems (LNP) (d ), Dubna, Kabardian-Balkarian State University (e ) and Austria
Institute of Applied Mathematics and Automation (f ), Nal’chik, Russia Technische Universität München, Germany
M. Cargnelli, H. Fuhrmann, P. Kienle, J. Marton, E. Widmann, J. Zmeskal
V.M. Abazovd , G. Alexeevd , A. Arefieva , M.Yu. Barabanova , B.V. Batyunyaa , D. Bogoslovskia , B. Ketzer, I. Konorov, A. Mann, S. Neubert, S. Paul, L. Schmitt, Q. Weitzel
T.Yu. Bokovaa , V.V. Borisova , V.A. Budilova Yu.V. Bugaenkoa , V.Kh. Dodokhova , A.A. Efremova , Soltan Institute for Nuclear Studies, Warsaw, Poland
Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, Germany
O.I. Fedorova , A.A. Feshchenkob , A.S. Galoyanb , G. Ivanova , E. Jafarova , V.I. Kaplina , A. Karmokove , Z. Guzik, M. Kisielinski, T. Kozlowski, D. Melnychuk, J. Wojtkowska, B. Zwieglinski
D. Frekers, A. Khoukaz, A. Täschner, J. Wessels
E.K. Koshurnikova , V.Ch. Kudaevf , V.I. Lobanova , A.F. Makarova , L.V. Malininaa , V.L. Malyshevd , Warsaw University of Technology, Institute of Atomic Energy, Otwock-Swierk, Poland
K.V. Mikhailova , B. Morosova , G.A. Mustafaeve , A.M. Nakhushevf , P.V. Nomokonova , I.A. Oleksa , Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics (BINP), Novosibirsk, Russia
B. Slowinski
V. Pismennayaa , T.A. Pocheptsova , A. Polanskic , G. Pontecorvod , A. Povtoreykoa , Yu.N. Rogovb , E. Baldin, V. Malyshev, A. Maslennikov, S. Peleganchyk, G. Pospelov, A. Sukharev, Yu. Tikhonov
a b
target spectrometer
I.A. Rufanov , S. Ryabtsun , Z.Ya. Sadygov , R.A. Salmin , A.G. Samartsev , M.G. Sapozhnikov ,
a b d b
T. Seredaa , G.S. Shabratovaa , A.A. Shishkind , A.N. Skachkovad , N.B. Skachkovd , E.A. Strokovskyb ,
Institut de Physique Nucléaire, Orsay, France
forward spectrometer
M. Guidal, T. Hennino, M. Mac Cormick, S. Ong, B. Ramstein, J. Van de Wiele, J. Pouthas, P. Rosier,
R.Sh. Tesheve , V. Tikhomirova , V.V. Tokmenind , E.P. Ustenkoa , V.V. Uzhinskyc , N.V. Vlasovb , T. Zerguerras
A.S. Vodopianova , S.A. Zaporozhetsa , N.I. Zhuravlevd A.I. Zinchenkoa Dipartimento di Fisica Nucleare e Teorica, Università di Pavia (a ), INFN, Sezione di Pavia (b ), Italy
University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom G. Bendisciolia,b , G. Bocaa,b , A. Fontanaa,b , P. Genovaa,b , L. Lavezzia,b , P. Montagnaa,b ,
M. Aliotta, D. Branford, K. Föhl, D. Watts, P. Woods A. Panzarasaa,b , A. Rotondia,b , P. Salvinib MUO
Friedrich Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Germany Institute for High Energy Physics (IHEP)( ), Protvino;
a
W. Eyrich, A. Lehmann Tomsk State University (TSU)(b ), Tomsk, Russia; Spokesperson: Ulrich Wiedner Email: ulrich.wiedner@tsl.uu.se
TOF Deputy: Paola Gianotti Email: paola.gianotti@lnf.infn.it
TPC
Northwestern University, Evanston, U.S.A. and National Center of Particle and High Energy Physics (NCPHEP)(c ), Minsk, Belorussia
K. Seth E. Ardasheva , Yu. Arestova , G. Ayzenshtatb , G. Britvicha , B. Chuikoa , S. Golovnyaa , S. Gorokhova ,
A. Kholodenkoa , V. Lishina , V. Parakhina V. Pikalova , V. Shelikhova , N. Shumeikoc , A. Solinc ,
SciFi
Università di Ferrara and INFN, Sezione di Ferrara, Italy O. Tolbanovb , A. Tyazhevb , A. Vorobieva
D. Bettoni, R. Calabrese, P. Dalpiaz, E. Luppi, M. Savriè
Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute of Academy of Science (PNPI), Gatchina, St. Petersburg, Russia
R. Dörner, R. Grisenti, M. Kaesz
SciFi
Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt, Germany S. Belostotski, G. Gavrilov, Y. Naryshkin, O. Miklukho, A. Sarantsev, V. Vikhrov
TOF Figure 1.3: Setup of the PANDA detector.
TAPAS
D. M. Kaplan, IIT TPC Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 5TAPAS Physics Case
in a nutshell:
}
• Hyperon CPV & rare decays
• Charmonium-like mystery states (XYZ...) World’s
best
• Charmonium spectrum exp’t!
• Charm mixing, CPV, & rare decays
+ (P̅ANDA) nuclear-physics topics: charmed hybrids &
glueballs, nuclear effects, hypernuclei, p!p Drell-Yan...
D. M. Kaplan, IIT TPC Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 6High-Rate Experiments!
• TAPAS: ≈20 to 50 MHz of charged particles
@ 10 MHz interaction rate
@ KE p! = 3.5–8 GeV
• P̅ANDA: ≈20 to 50 MHz of charged particles
@ (ultimately) 10 MHz interaction rate
@ KE p! = 1–14 GeV
• Based on NA-48/2 KABES (tested to 70 MHz),
TPC can handle this with MPGD readout
(Micromegas or multi-GEM)
D. M. Kaplan, IIT TPC Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 7KAon BEam Spectrometer
NA48/KABES
Tdrift2
! "#$%&$'()*+*,"-*.*/$�/)123 Micromegas
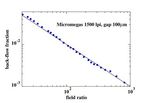
! 4(56*7689:;&/;&/Results from Micromegas TPC R@D
!= 40 µm
M. Dixit et al., Spatial resolution
Pad size = 2 mm
P. Colas et al., NIM-A 535 (2004) 226
With 1.5 x 4 mm2 pads,
we expect we can have 32 pad rows
with a resolution of about 50 µm
D. M. Kaplan, IIT TPC Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 9TPC Option 1?
TAPAS
Superconducting
solenoid
TOF
Cylindrical
SciFi
TPC TOF
• Expected interaction rate ≈10 MHz @ 8 GeV p! K.E.
Figure 6: E835 apparatus layout (from [67]).
• Expected track rate up to 50 MHz
≈ 1 kB per event with SciFi tracking
• TPC, L ≈ 1 m ≈8 µs memory ≈80 events pile-up!
data per event ≈ 3 MB?!
D. M. Kaplan, IIT TPC Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 10TPC Option 2?
TAPAS
Superconducting
solenoid
TOF
TPC
SciFi
TOF
• Expected interaction rate ≈10 MHz @ 8 GeV p! K.E.
Figure 6: E835 apparatus layout (from [67]).
• Expected track rate up to 50 MHz
≈ 1 kB per event with SciFi tracking
• TPC, L ≈ 0.15 m ≈1.2 µs memory ≈12 events pile-up
data per event ≈ 30 kB?
D. M. Kaplan, IIT TPC Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 11Data Rate
• Expect Level 1 Trigger Accept rate ≈100 kHz
• Pass tracker data to Level 2 Trigger
• SciFi option: needed bandwidth ≈100 MB/s
• TPC option 1: needed B/W ≈30 TB/s!
• TPC option 2: needed B/W ≈ 3 GB/s – OK
D. M. Kaplan, IIT TPC Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 12TPC Specs
• Must minimize pile-up &
space-charge effects
want high drift speed
• CH4 @ 900 V/cm suitable
vdrift ≈12.5 cm/µs
• Say
rin = 2 cm,
rout = 15 cm,
L = 15 cm
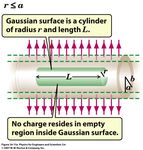
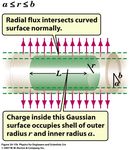
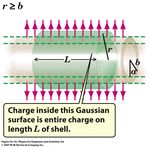
D. M. Kaplan, IIT TPC Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 13Space Charge
• At high particle rate, drifting ions will perturb
drift field due to space charge
• Rough (over?)estimate:
-
treat as cylinder of charge with inner radius a,
r = 15 cm
outer radius b:
! !
( ) ( ) r = 2 cm
TPC
E= r #a
2 2
E= b #a
2 2
p! beam
2" 0 r 2" 0 r 21
• Plausible parameter values: L = 15 cm
ρ = 800 nC/m3, r = b = 0.03 m, a = 0.02 m
< KABES
E(r = 3 cm) ≈ 800 V/m = 8 V/cm
D. M. Kaplan, IIT
- small w.r.t. 900 V/cm drift field
TPC Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 14Summary
• Best experiment ever on hyperons, charm, and
charmonia may soon be feasible at Fermilab
- including world’s most sensitive charm CPV study?
• World’s best p̅ source → simple way to broad
physics program in (pre-)Project X era
• Can small high-rate TPC cost-effectively improve
experiment performance?
(For more info see http://capp.iit.edu/hep/pbar/.)
D. M. Kaplan, IIT TPC Challenges TIPP 2011, 11 June 2011 15You can also read