The protective effect of coenzyme Q10 on experimental diabetic nephropathy in male rats
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
EurAsian Journal of BioSciences
Eurasia J Biosci 14, 5823-5828 (2020)
The protective effect of coenzyme Q10 on experimental
diabetic nephropathy in male rats
Maryam I. Salman 1*, Rashied M. Rashied 2, Hala M. Hamad 1, Hajir SH. Hamad 1
1
Department of Biology, College of Science, University of Anbar, IRAQ
2
Department of Biotechnology, College of Science, University of Anbar, IRAQ
*Corresponding author: Maryam I. Salman
Abstract
Background: Diabetes causes increased reactive oxygen production which results in sever oxidative
stress finally leads to diabetic complication including Diabetic Nephropathy, Coenzyme Q10 is a
natural antioxidant helping the body get rid of the effect of free radicals, the current study examined
the beneficial effect of Coenzyme Q10 against Diabetic Nephropathy DN.
Materials and Methods: Twenty male Wister rats were used in this study, rats were allocated in four
identical group (five per each) the first group administrated distill water (0.5 ml) and considered as
control group, the second administrated Coenzyme Q10 by10 mg ̸ kg and considered as CoQ10
group, the third group were injected intravenously with 42 mg/kg Alloxan and considered as untreated
diabetic group, the forth one was treated diabetic group in which rats were given Alloxan and
Coenzyme Q10, treatment were repeated every day for eight weeks.
Results: The result illustrated that Alloxan treatment caused significant increase in urea, creatinine
as well as uric acid concentration P ≤ 0.05. In addition Alloxan treatment caused a clear
histopathological changes in kidney including acute cellular degeneration, tubular vacuolization,
glomerular atrophy and Bowmanˈs capsule dilation. Treatment with Coenzyme Q10 significantly
decrease urea, creatinine as well as uric acid concentration P ≤ 0.05, in addition to clear improvement
in renal tissue.
Conclusions: CoQ10 could offer a beneficial protective effect against Alloxan-induced diabetic
nephropathy in male rats, administration of Coenzyme Q10 can prevent or delay diabetic
nephropathy.
Keywords: diabetic Nephropathy, coenzyme Q10, kidney, urea, diabetes
Salman MI, Rashied RM, Hamad HM, Hamad HSH (2020) The protective effect of coenzyme Q10
on experimental diabetic nephropathy in male rats. Eurasia J Biosci 14: 5823-5828.
© 2020 Salman et al.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
INTRODUCTION oxidative stress is also responsible for the development
of DN (Matough et al. 2012, Xiaofeng et al. 2019).
Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) is a serious renal disease Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) or ubiquinone is a fat-soluble
related to diabetes and it’s a major complication of vitamin-resemble quinone that play an essential role in
diabetes which led to chronic renal disease in addition to ATP generating in mitochondria, reduction of reactive
end stage renal failure, about 25 of persons with oxygen species and activating the mitochondrial
diabetes finally develop kidney disease(Lim 2014, enzymes (Ozaltin 2014), in addition it has the ability to
Barnett 2006). In hyperglycemia state, a non-enzymatic inhibit the lipids peroxidation in the cell membrane and
reaction accrue between sugar and the free amino work as antioxidant outside the membrane of the
groups of ingredients called glycation this results in mitochondria also it has the ability to resist the initiation
chemical, cellular and histological changes and leads to of free radicles (Lance et al. 2012).
nephropathy, the glycation reaction is reversible causing The plasma levels of CoQ10 are decreased In
the early glycation products (EGPs) formation, if patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD)
hyperglycemia continuous this glycation reaction (Mehametoglu et al. 2012). CoQ10 have beneficial
become reversible and causing the development of influences on hypertension, cardiac function, lipid
advanced glycation end products (AGEs) which induce profile, glucose metabolism, oxidative stress and
charge, conformation and solubility of extra cellular inflammation in patients with non-dialysis CKD and
matrix (ECM) (Pourghasem et al. 2014). On another
hand it has been found that the diabetic kidney diseases
Received: May 2019
was associated with vasodilatation abnormalities and
Accepted: April 2020
generation of reactive oxygen species mediated by
Printed: November 2020
endothelial derivative nitric oxide (NO) proposing that
5823EurAsian Journal of BioSciences 14: 5823-5828 (2020) Salman et al.
dialysis (Xu et al. 2019). CoQ10 administration
significantly better metabolic profile in CKD patients by
decreasing total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, MDA as
well as creatinine concentrations (Bakhshayeshkaram et
al. 2018). The aim of this study was to assess the Reno
protective influence of CoQ10 on Alloxan prompted
diabetic nephropathy in male rats by measuring urea,
creatinine and uric acid concentration and by assessing
the ability of Co Q10 in improving renal tissue worsening.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Experimental Animals and Induction of Fig. 1. The influence of CO Q10 on Fasting Blood
*p˂0.05 when compared with control and CO Q10 group.
Diabetic Nephropathy *p˂0.05 when compared with control and CO Q10 group
The study included twenty male Wister rats, weighing
200-250g gained from Al-Nahrain University
Biotechnology Research Center. The rats were placed
in metal cages in a standard laboratory condition at 27ºC
with controlling lighting and exhaust with free contact to
water and food, they were divided to four groups (five
per each): group 1 as non-diabetic control, group 2 as
Coenzyme Q10 in which rats were given Co Q10 by10
mg/kg that was dissolved in distill water via stomach
tube, group 3 as untreated diabetic in which diabetes
mellitus was stimulated by a single intravenous dose of
42 mg /kg of newly prepared solution of Alloxan
monohydrate in the tail veins and group 4 as treated Fig. 2. The influence of CO Q10 on serum urea Sugar in
diabetic in which the diabetic rats given Co Q10 by10 the studied group in the studied group
*#p˂0.05 when compared with diabetic group.
mg/kg, treatment was started at the same day of diabetic *#p˂0.05 when compared with diabetic group.
induction, the induction of diabetes mellitus was
confirmed five day after treatment with Alloxan by using Statistical Analysis
blood glucometer, rats with FBG level above 250 mg ̸ dl All the statistical analyses of the study were done via
were considered as diabetic. the statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS)
Biochemical Parameters version 23.0, comparison between groups were done
At the end of the eighth week of treatment all animals using one way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple range
were anesthetized using (ketamine 100 mg ̸ kg and tests. A probability p value fewer than 0.05 was reflected
xylazine 50 mg ̸ kg, i.m.). Blood sample were took from significant difference. values are stated as mean ±
heart, clot for twenty minute in room temperature then standard deviation.
centrifuged at 3000 rpm for ten min for serum collecting.
Renal function test were done on a multi chemical fully RESULTS
automated chemistry analyzer using different
The mean of FBS in control, CO Q10, diabetic and
commercial kits, measurement of urea was carried out
diabetic + CO Q10 group were 83.24±20.5, 79.27±10.2,
using enzymatic (urease) kinetic method, jaffe kinetic
300.05±40.3 and 220.08±32.6(mg/dl) respectively
method was used for measuring creatinine. For the
(Fig.1).
determination of serum uric acid, enzymatic (uricase)
The mean level of urea in control group was 22.5
method was done. serum level of fasting blood glucose
±1.23 (mg/dl), in CO Q10 group the mean level was
(FBG) was determined using LINEAR CHEMICALS S.L.
22.1±1.04 (mg/dl), while the mean levels was 55.7±2.81
(Barcelona, Spain).
(mg/dl) and 34.7±1.2 (mg/dl) in diabetic and diabetic +
Histological Examination CO Q10 group respectively (Fig.2). The mean of
Kidneys were dissected, rinsed in saline and creatinine in control, CO Q10, diabetic and diabetic + CO
immersed in formalin solution 10% for 24 hours for Q10 group were 0.68±0.03, 0.65±0.05, 1.92±0.07 and
fixation, ascending alcohol solution were used for drying 1.2±0.02 respectively (Fig.3), the mean of uric acid in
the fixed samples, specimen were cleared in xylene, control, CO Q10, diabetic and diabetic + CO Q10 group
embedded inside paraffin blocks and sectioned at five were 2.03±0.12, 2±0.32, 4.92 ± 0.41 and 3.15±0.19
µm using microtome. The slides were stained using (mg/dl) respectively (Fig.4).
Hematoxylin and Eosin stains and studied by light
microscope.
5824EurAsian Journal of BioSciences 14: 5823-5828 (2020) Salman et al.
Fig. 3. The influence of CO Q10 on serum creatinine
*p˂0.05 when compared with control and CO Q10 group.
*p˂0.05 when compared with control and CO Q10 group (a)
Fig. 4. The influence of CO Q10 on serum uric acid in the
(b)
studied group in the studied group
*#p˂0.05when compared with diabetic group.
*#p˂0.05 when compared with diabetic group.
(c)
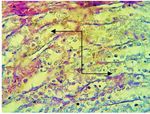
Fig. 6. Section in the kidney of diabetic group shows acute
(a) cellular degeneration characterized by severe vacuolation,
desquamation of epithelial cells of renal tubules (a), with
atrophy of glomerular vtufts with dilated of Boman space
(b), with mononuclear cells infiltration in the interstitial
tissue (c) (H &E stain 400X)
compare to control and CoQ10 group, Co Q10 treatment
significantly improve (P ≤ 0.05) FBG, urea, creatinine as
well as uric acid when compare to diabetic group (Figs.
1-4).
Histological Studies
The histological examination of the normal control
kidney group showed normal appearance of glomeruli
(b) and tubules (Fig.5 a,b). The diabetic group kidney
Fig. 5. a,b.Section in the kidney of control group shows no showed sever tissue damage including acute cellular
clear lesions (H &E stain 400X) degeneration characterized by sever vacuolation,
desquamation of epithelial cells of renal tubules (Fig.
Alloxan treatment significantly increase (P ≤ 0.05) 6a), atrophy of glomerular tufts, dilation of bowman
FBG, urea, creatinine as well as uric acid, when space (Fig.6b) and mononuclear cells infiltration in
5825EurAsian Journal of BioSciences 14: 5823-5828 (2020) Salman et al.
such us vitamin E (Roldi et al. 2009), vitamin C (Aluwong
et al. 2016), lipoic acid (Balkis et al. 2009, Winiarska et
al. 2008), melatonin (Garfinkel et al. 2011), caffeic
acid(21) and other natural compound like onion extract
(Nurcahyawati et al. 2017). Tabrizi and Mohajeri (2011)
demonstrated that the diabetic rats induced by Alloxan
suffer from increasing amount of Malondialdehyde in
their renal tissue this exposed that the oxidative stress
triggered by free radicles was one of the main
mechanisms complicated in diabetic nephropathy.
Ahmadvand (2012) reported that coenzyme Q10 has
valuable effects in decreasing hemoglobin A1c, urea as
(a) well as creatinine in alloxan induced diabetic rats.
Maheshwari etal. (2014) indicated that co-administration
of coenzyme Q10 with metformin significantly reduced
HbA1c, urea, creatinine, uric acid and can diminish the
renal histological deteriorations in comparison to
diabetic rats, also the authors concluded this therapy
could prevent or delay the diabetic nephropathy. Khalifa
et al. (2020) demonstrated the beneficial effect of
combing coenzyme Q10 plus alpha lipoic acid in
preventing the toxic renal damage in cisplatin- induced
nephrotoxicity in rats.
After eight weeks of diabetes initiation the animals
kidney demonstrated a clear histological derangement
(b) including acute cellular degeneration, tubular
Fig. 7. a,b. Section in the kidney of CO Q10+ diabetic vacuolization, glomerular atrophy and Bowmanˈs
shows no clear lesions (H &E stain 400X) capsule dilation. The vacuolar changes may refer to the
interstitial renal tissue (Fig.6c). The treated diabetic initiation of Armanni- Ebstein lesion which related to
kidney group showed no clear lesions (Fig7a,b). glycogen deposition and sub nuclear lipid vacuolization
(Lau et al. 2012). Pourghasem etal. (2014) study the
DISCUSSION early nonglumerular histological changes in Alloxan
induced diabetic rats which include the deposition of
Diabetic nephropathy is the major cause of chronic
eosinophilic materials in the intermediate substantial in
kidney failure worldwide and it is the leading cause of
medulla in addition to vacuolar changes in the tubular
kidney failure in around one third of patients who were
cells of all diabetic kidney, also they indicated an
under dialysis (Dabla 2010). In the present study
increasing in kidney weight when compared to control
diabetes significantly increase serum glucose, urea,
rats.
creatinine as well as uric acid when compared to control
Marasha and Hejazi (2015) demonstrated that the
group, treatment of animals with CoQ10 significantly
treatment of Alloxan prompted diabetic rats with
decrease all these variables and inhibited the
coenzyme Q10 can meaningfully reduce
progression of diabetic nephropathy. High
glomerulonephritis, tubular necrosis and nephrosis and
concentrations of serum glucose, creatinine, urea as
they indicated that the administration of coenzyme Q10
well as uric acid are the marker of diabetic nephropathy
can prevent the side effects of diabetes on kidney.
development (Idonije et al. 2011, Morsy et al. 2010).
There are several studies reported that oxidative stress
CONCLUSION
play a chief part in the pathogeneses and complication
of diabetes via production of free radicles like Coenzyme Q10 has a positive effect in reducing the
superoxide and lipid peroxidation product such us elevated serum urea, creatinine and uric acid
Malondialdehyde which induced tissue damage concentration, in addition it has a beneficial effect in
(Ahmadvand et al. 2012, Jamor et al. 2019). On the recovery from diabetic nephropathy, the administration
other hand many studies indicate the protective effect of of coenzyme Q10 can prevent the side effect of diabetes
many antioxidant against tissue damage in diabetes on kidney.
5826EurAsian Journal of BioSciences 14: 5823-5828 (2020) Salman et al.
REFERENCES
Ahmadvand H, Khodai M, Khosrowbeygi A.(2012). Amelioration of altered antioxidant enzymes activity and
glomerulosclerosis by coenzyme Q10 in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Journal of diabetes and its complications
26: 476-482.
Ahmadvand H (2012). Effects of Coenzyme Q10 on Hemoglobin A1C, Serum Urea and Creatinine in Alloxan-
Induced Type 1 Diabetic Rats. Iranian Journal of Pharmacology & Therapeutics 11(2):64-67.
Aluwong T, Ayo JO, Kpukple A, Oladipo OO.(2016). Amelioration of Hyperglycaemia, Oxidative Stress and
Dyslipidaemia in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats Treated with Probiotic and Vitamin C. Nutrients 8(5): 151
Bakhshayeshkaram M, Lankarani KB, Mirhosseini N, Tabrizi R, Akbari M, Dabbaghmanesh MH, Asemi Z.
(2018).The Effects of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Metabolic Profiles of Patients With Chronic Kidney
Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. 24(31):3710-3723.
Balkis Budin S, Othman F, Louis SR, Abu Bakar M, Radzi M, Osman K, Das S, Mohamed J. (2009).Effect of alpha
lipoic acid on oxidative stress and vascular wall of diabetic rats. Romanian journal of morphology and embryology
50:23-30.
Barnett A. (2006).Prevention of Loss of Renal Function Over Time in Patients With Diabetic Nephropathy. Am J 119:
40-47.
Dabla PK.(2010). Renal Function in Diabetic Nephropathy. 1(2):48-56.
Garfinkel D, Zorin M, Wainstein J, Matas Z, Laudon M, Zisapel N.(2011). Efficacy and safety of prolonged-release
melatonin in insomnia patients with diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, crossover study. Diabetes Metab
Syndr Obes 4: 307–313.
Idonije BO, Festus O, Oluba OM. (2011).Plasma Glucose, Creatinine and Urea Levels in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Attending A Nigerian Teaching Hospital.;5:1-3.
Jamor P, Ahmadvand H, Ashoory H, Babaeenezhad E.(2019),Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on antioxidant gene
expression and kidney injury in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. 8(1):e06.
Jung UJ, Lee MK, Park YB, Jeon SM, Choi MS.(2006). Antihyperglycemic and antioxidant properties of caffeic acid
in db/db mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 318(2):476-83.
Khalifa EM, Ahmed AN, Hashem KS, Gad Allah A. (2020).Therapeutic Effects of the Combination of Alpha-Lipoic
Acid (ALA) and Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) on Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. International Journal of
Inflammation Article ID 5369797.
Lance J, McCabe S, Clancy RL, Pierce J. (2012).Coenzyme Q10--a therapeutic agent. Medsurg Nurs 21(6):367-
371.
Lau X, Zhang Y, Kelly DJ, Stapleton D. (2012).Attenuation of Armanni-Ebstein lesions in a rat model of diabetes by
a new anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory agent, FT011. Diabetologia 56(3):675-679.
Lim A KH. (2014).Diabetic nephropathy – complications and treatment. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis 2014; 7: 361–
381.
Maheshwari RA, Balaraman R, Sen AK, Seth AK.(2014). Effect of coenzyme Q10 alone and its combination with
metformin on streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats Indian J Pharmacol 46(6):627-
632.
Marashi M, Hejazi S. (2015).The protective effect of coenzyme Q10 on nephropathy in Alloxan-induced diabetic rats.
4(2):39-46.
Matough FA, Budin SB, Hamid ZA, Alwahaibi N, Mohamed J. (2012).The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in
diabetic complications. 12(1):5-18.
Mehmetoglu I, Yerlikaya FH, Kurban S, et al.(2012). Oxidative stress markers in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis
patients, including coenzyme Q10 and ischemia-modified albumin. Int J Artif Organs 35:226–32.
Morsy MD, Hassan WN, Zalat SI. (2010).Improvement of renal oxidative stress markers after ozone administration
in diabetic nephropathy in rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2: 29.
Nurcahyawati DG, Plumeriastuti H, (2017) Maslachah. protection of dayak onion tuber extract (Eleutherine
palmifolia) against kidney histopathological appearance of albino male rat strain wistar which was induced by
alloxan. The Veterinary Medicine International Conference
Ozaltin F.(2014). Primary coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) deficiencies and related nephropathies. Pediatr Nephrol 29:961-
969.
5827EurAsian Journal of BioSciences 14: 5823-5828 (2020) Salman et al.
Pourghasem M, Nasiri E, Shafi H. (2014).Early renal histological changes in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Int J Mol
Cell Med 3(1):11-5.
Pourghasem M, Nasiri E, Shafi H.(2014). Early Renal Histological Changes in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. Int J
Mol Cell Med 3(1):11-15.
Roldi LP, Pereira RV, Tronchini EA, Rizo GV, Scoaris CR, Zanoni JN, Natali MR. Vitamin E (2009).(alpha-
tocopherol) supplementation in diabetic rats: effects on the proximal colon. BMC Gastroenterol 23:88.
Tabrizi BA, Mohajeri D. (2011).Protective effect of turnip root ethanolic extract on early diabetic nephropathy in the
rats. Zahedan Journal of Research in Medical Sciences 13(6):13-19.
Winiarska K, Malinska D, Szymanska K, Dudziak M, Bryla J. (2008).Lipoic acid ameliorates oxidative stress and
renal injury in alloxan diabetic rabbits. 90(3):450-459.
Xiaofeng Z, Zhaofeng S, Qian L, Haohao Q, Xiaohong C. (2019).Effects of coenzyme Q10 intervention on diabetic
kidney disease A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 98 (24)- p e15850.
Xu Y, Liu J, Han E, Wang Y, Gao J.(2019). Efficacy of coenzyme Q10 in patients with chronic kidney disease:
protocol for a systematic review. BMJ 9:e029053.
www.ejobios.org
5828You can also read