KERNEL Issue 7, 2021 - Indian Institute of Science
←
→
Page content transcription
If your browser does not render page correctly, please read the page content below
Research Newsletter of
the Indian Institute of Science Issue 7, 2021
KERNEL
Editorial TAKING THE QUANTUM LEAP
Quantum technologies have
already leaped into our lives,
powering the appliances,
digital cameras, computers
and GPS we use everyday.
At IISc, diverse researchers
are coming together to help
nudge India’s quantum
ambitions forward. Read Cartoon of a device used for single photon detection with 2D materials (Image: Arindam Ghosh)
more about their efforts in A NEW INITIATIVE AT IISc ENVISIONS A CRUCIAL ROLE IN
this issue of Kernel. INDIA’S QUANTUM QUEST
Quantum mechanics – the physics of witnessed what is now called the first
Our lab feature uncovers the subatomic particles – underlies all that we quantum revolution – technological
work that goes into building currently know about atoms, what they are breakthroughs such as semiconductors,
made of and why they behave the way they MRI imaging, lasers and so on.
drones for healthcare and do. But it is not just a physicist’s tool to try
other applications. We also and understand the universe at extremely Many believe that we are presently
include stories on a blood small scales. The devices that you are most living through the second quantum
likely using to read this article – computers revolution. The era of ‘quantum
biomarker for differentiating and smartphones – also rely on technologies technologies’ has arrived with many
bacterial from viral infections that operate on quantum mechanical promises – sensors and measurement
and the discovery of electron phenomena. devices with unprecedented precision,
secure communications via what is
species that could provide The modern semiconductor-based electronics called the “quantum internet”, and
interesting insights into industry is entirely dependent on our quantum computers capable of solving
material properties. understanding of the quantum nature of problems far beyond the scope of existing
matter. The second half of the 20th century supercomputers.
Continued on page 2Refrigerator to protect superconducting qubits from thermal and ambient noise. L: Students preparing system for cooldown, R: Inside of fridge with microwave cables
Continued from page 1 (Photos courtesy: Vibhor Singh)
“The new term ‘quantum technology’ is Measuring magnetic fields with greater qubits – platforms that are being
connected to unique applications of quantum precision, for example, can lead to smaller explored worldwide to build large-
mechanics or of quantum mechanical principles, MRI machines that will produce images with scale quantum computers. Qubits or
which were by and large ignored in our better clarity while using lower radiation quantum bits are the basic data units
technological advances during the last 100 doses. of a quantum computer, analogous to
years,” says Arindam Ghosh, Professor in the bits in its digital counterparts. Although
Department of Physics, IISc. Research related to such quantum companies like Google and IBM have
technologies has been going on at IISc for managed to create superfast devices
In recent years, research on quantum technology a long time but in a disconnected manner, having 53-54 qubits, Singh points out
has received a massive boost worldwide. A USD in individual laboratories. In 2019, Patel that the more fundamental problems,
1.13 billion quantum technologies project was along with several others received generous like finding the best strategy to scale
announced by the EU in 2016 and a national funding from the Ministry of Electronics up qubits, remain unsolved. His team is
quantum initiative worth USD 1.2 billion was and Information Technology (MeitY), trying to come up with small prototype
launched by the US in 2018. Russia followed suit Government of India, to establish the Center systems – working at the level of
in 2019 by committing USD 790 million towards for Excellence in Quantum Technology at single or two qubit devices – which,
basic and applied quantum technology research. IISc, partnering with the Raman Research if successful, might help in scaling up
Institute (RRI) and Center for Development the number of qubits faster and in a
India is not too far behind. The Government of Advanced Computing (CDAC). IQTI, which more straightforward manner. In fact,
of India announced the National Mission on will now consolidate all quantum technology- building an 8-qubit quantum processor
Quantum Technologies and Applications (NM- related research in the Institute, is the first is something IQTI hopes to achieve in
QTA) in 2020 – to encourage both fundamental such large-scale initiative in the country, the near future.
and applied research in the country – and has according to Patel and Ghosh, with well
proposed to allocate Rs 8000 crore over a span defined short- and long-term goals. Patel and his team also played a crucial
of five years. IISc too has taken a step forward role in developing QSim, a Quantum
in this direction. The IISc Quantum Technology IQTI aims to establish a framework which will Computer Simulator Toolkit, which was
Initiative (IQTI), launched in November 2020, promote collaborations between physicists, launched by MeitY in August 2021. A
aspires to lay a solid foundation for quantum computer scientists, material scientists and collaborative effort by IISc, IIT Roorkee,
technology within the Institute, and contribute engineers. Currently, more than 40 faculty and CDAC, this educational toolkit seeks
to the country’s R&D efforts. members from diverse departments are to help students and researchers in
part of the initiative. “This also involves the country write and debug quantum
If you are wondering why governments people who are not necessarily connected code, which is essential for developing
worldwide have taken such an interest in to quantum [research], but they may have quantum algorithms.
quantum technologies, the answer lies in the technology or materials which can be
outcomes that they promise. The anticipated immediately utilised in the development of Another highlight of IQTI is a two-year
technological advances can impact many socio- quantum technologies,” says Ghosh. IQTI will MTech degree programme in Quantum
economic sectors – molecular and material focus on four broad areas: quantum sensing Technology – the first of its kind in
design can transform sensors, healthcare, and metrology, quantum communications India – which admitted its first batch of
pharmaceuticals, agriculture and engineering; and cryptography, quantum materials and students in August 2021.
secure communications can benefit finance and devices, and quantum computation and
defense services, and so on. simulations. Patel points out how the country’s
nuclear and space programmes were
“Simple examples which are already in place One goal is to establish a campus-wide conceived and nurtured at IISc decades
include the atomic clock which, by using quantum-secured communication network ago. “However, to develop them from
quantum technology, has improved by orders of within the next 4-6 years. “Quantum theory scratch to a level that is comparable
magnitude in precision and accuracy – its direct allows you to transmit signals in a way that is to the best in the world, it took India
consequence being a significant improvement protected from eavesdroppers or interceptors almost 50 years. Huge efforts are
in the GPS resolution,” explains Apoorva Patel, in the middle, by a process where – if there is required both in terms of manpower as
Professor at the Center for High Energy Physics any interception – the receiver will know that well as towards building infrastructure.
(CHEP), IISc, who is one of the faculty members the signal has been compromised,” explains The long-term vision for IQTI is to do
leading IQTI. Patel. something similar for India in quantum
technology.”
Another advancement that is likely to happen Research related to quantum computing is
soon, he adds, is improved precision in the also happening in the lab of Vibhor Singh,
measurement of magnetic and electric fields, Assistant Professor in the Department of - Sritama Bose
giving rise to many practical applications. Physics, who works with superconducting
KERNEL | ISSUE 7, 2021 | Pg 2Image: Sathyabaarathi Ravichandran
BLOOD-BASED BIOMARKER TO
DISTINGUISH BETWEEN BACTERIAL
AND VIRAL INFECTIONS
SUCH A SIGNATURE CAN POTENTIALLY HELP CLINICIANS OPTIMISE TREATMENT AND AVOID INDISCRIMINATE
USE OF ANTIBIOTICS
A recent study has identified a set of the rise of such antimicrobial resistance. The authors suggest that the test could
molecular biomarkers that can be used in In their new study, published in the be useful for differentiating COVID-19
the differential diagnosis of acute bacterial journal EBioMedicine, the researchers infection from bacterial infections as well.
and viral infections. The biomarkers are have developed such a test using patient In the study, they looked at various viral
messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules found blood transcriptomes and sophisticated infections for which transcriptomic data
in the blood; differences in their levels can computational modelling. is publicly available. This allowed them
predict with high probability if an infection to develop a generic VB10 test score for
is viral or bacterial. A transcriptome is a full set of mRNA viral infections. As soon as transcriptomic
molecules expressed by a biological cell, data became available for COVID-19, the
The human body responds to bacterial and which is measured using Next-Generation team tested their approach and found
viral infections differently, by producing Sequencing (NGS) technologies. that the test scores could differentiate
specific types of molecules – such as During an infection, specific genes are between SARS-CoV-2 infection and common
proteins and RNA – in the blood. While turned on, leading to an increase in the bacterial respiratory infections.
antibiotics can treat bacterial infections, production of specific mRNAs and their
they are ineffective against viral infections. corresponding proteins. The scientists This work was done in collaboration with
However, indiscriminate use of antibiotics analysed transcriptomic data of patients clinicians at MS Ramaiah Medical College
to treat any kind of infection has given rise (from publicly available databases, and and researchers Amit Singh, Dipshikha
to bacterial strains that are now resistant to samples collected from MS Ramaiah Chakravortty and KN Balaji at IISc. The
our entire arsenal of antibiotics. “Antibiotics Medical College in collaboration with a team hopes to begin a trial study to
are given even for viral infections in some clinical team) and discovered a 10-gene translate their research from the lab to
cases because of misdiagnosis. With current RNA signature in the patients’ blood that the clinic. “This test can be done using
methods, it can take a lot of time to test is produced in varying quantities for viral qRT-PCR. Given how common RT-PCR has
for bacterial or viral infections,” explains and bacterial infections. become due to the pandemic, getting this
first author Sathyabaarathi Ravichandran, test off the ground should not pose a major
Research Associate in the lab of Nagasuma To enable it to be used in clinical practice, challenge,” says Chandra. The researchers
Chandra, Professor in the Department of the researchers devised a standalone expect it to be useful early on during the
Biochemistry. score called VB10, which could be used infection, and work against any strain.
for diagnosis, monitoring the stage of This can supplement the current COVID-19
A quick method to detect acute viral and recovery after infection, and estimating diagnosis tests.
bacterial infections and distinguish between the severity of the infection. VB10
them can be immensely useful in the clinic, accurately indicated whether a given
as accurate diagnosis will win half the blood sample had a bacterial or viral - Debayan Dasgupta
battle and guide the clinician towards the infection, across different bacteria and (with input from authors)
optimal treatment path. It will also prevent viruses and across different age groups.
KERNEL | ISSUE 7, 2021 | Pg 3Image: Neha Yadav
DISCOVERY OF FEW ELECTRON
BUBBLES IN SUPERFLUID HELIUM
THEY CAN PROVIDE INSIGHTS INTO HOW MATERIAL PROPERTIES ARE INFLUENCED BY ELECTRON INTERACTIONS
Researchers at IISc have experimentally understanding how FEBs are formed “FEBs form an interesting system that
shown the existence of two species of can also provide insights into the has both electron-electron interaction
few electron bubbles (FEBs) in superfluid self-assembly of soft materials, which and electron-surface interaction,”
helium for the first time. These FEBs can can be important for developing next- Yadav explains.
serve as a useful model to study how the generation quantum materials. However,
energy states of electrons as well as the scientists have only theoretically There are several phenomena that
interactions between them in a material predicted the existence of FEBs so far. can be deciphered through FEBs, such
influence its properties. “We have now experimentally observed as turbulent flows in superfluids and
FEBs for the first time and understood viscous fluids, or the flow of heat in
The team included Neha Yadav, a former how they are created,” Yadav says. superfluid helium. In the same way
PhD student at the Department of Physics, “These are nice new objects with great that current flows without resistance
Prosenjit Sen, Associate Professor at the implications if we can create and trap in superconducting materials at very
Centre for Nano Science and Engineering them.” low temperatures, superfluid helium
(CeNSE) and Ambarish Ghosh, Professor also conducts heat efficiently at very
at CeNSE. The study was published in Yadav and colleagues were studying the low temperatures. But defects in the
Science Advances. stability of MEBs at nanometre sizes system, called vortices, can lower its
when they serendipitously observed thermal conductivity. Since FEBs are
An electron injected into a superfluid FEBs. “It took a large number of present at the core of such vortices
form of helium creates a single electron experiments before we became sure that – as the authors have found in this
bubble (SEB) – a cavity that is free of these objects were indeed FEBs. Then it study – they can help in studying
helium atoms and contains only the was certainly a tremendously exciting how the vortices interact with each
electron. There are also MEBs – multiple moment,” says Ghosh. other, and how heat flows through the
electron bubbles that contain thousands superfluid helium.
of electrons. The researchers first applied a voltage
pulse to a tungsten tip on the surface “In the immediate future, we would
FEBs, on the other hand, are nanometre- of liquid helium. Then they generated a like to know if there are any other
sized cavities in liquid helium containing pressure wave on the charged surface species of FEBs, and understand
just a handful of free electrons. The using an ultrasonic transducer. This the mechanisms by which some are
number, state and interactions between allowed them to create 8EBs and 6EBs, more stable than the others,” Ghosh
free electrons dictate the physical two species of FEBs containing eight and says. “In the long term, we would
and chemical properties of materials. six electrons respectively. These FEBs like to use these FEBs as quantum
Studying FEBs, therefore, could help were found to be stable for at least 15 simulators, for which one needs to
scientists better understand how some milliseconds (quantum changes typically develop new types of measurement
of these properties emerge when a few happen at much shorter time scales) schemes.”
electrons present in a material interact which would enable researchers to trap
with each other. According to the authors, and study them. - Joel P Joseph
KERNEL | ISSUE 7, 2021 | Pg 4Photo: Stefan Greif
EAVESDROPPING BATS TAKE LONGER TO CAPTURE
CRICKETS CALLING IN GROUPS
In a new study, Harish Prakash and Rohini The researchers also found that bats took to target and capture an individual
Balakrishnan from the Centre for Ecological considerably longer to capture a katydid when it is among many others.
Sciences (CES), with collaborators from Tel calling in a group of three than a lone
Aviv University, explored whether calling katydid. This delay gives the katydid an Previous studies have looked at this
in a group reduces risk for katydids (bush opportunity to stop calling, and escape only in visual predators like monkeys,
crickets) against bats, which are their from being eaten. Therefore, although a geckos and fish. This study provides
predators. They found that bats were more chorus of katydids can attract bats, the the first evidence of an auditory
attracted to three speakers simultaneously bats’ inefficiency in capturing them when confusion effect in eavesdropping
playing katydid calls than a single speaker. they are in groups can benefit the prey. predators such as bats.
Does this mean calling together in a group
might be riskier? Yes. But that is just one A possible reason for the delay is the - Harish Prakash
part of the story. confusion effect: it is harder for a predator
Image courtesy: Raghavan Varadarajan
FIGHTING COVID-19 VIRAL VARIANTS WITH
A HEAT-TOLERANT VACCINE
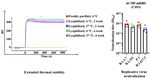
A ‘warm’ COVID-19 vaccine candidate being their neutralising ability against the losing its shape, and withstand
developed by an IISc and Mynvax team was variants by researchers at CSIR-IMTech, transient exposure to temperatures
found to trigger a strong immune response Chandigarh and the Australian Centre as high as 100°C; this was also true
and protection in mice and hamster for Disease Preparedness, run by CSIRO, of the current, improved versions.
models, in results published recently Australia’s national science agency. Such vaccines are especially useful
in ACS Infectious Diseases. Crucially, in countries like India where cold
the vaccine formulation also triggered The vaccine candidate has been designed storage and transportation are
neutralising antibodies – those that bind by genetically engineering the Receptor expensive and challenging. One
to the virus and prevent infection – against Binding Domain (RBD) of the surface of the improved formulations is
all four current SARS-CoV-2 variants of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2. being rapidly moved to clinical
concern: Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta. development.
In previous reports, an earlier version
The vaccinated sera (blood) samples of the vaccine candidate was found to
from animal models were tested for be stable at 37°C for a month without
KERNEL | ISSUE 7, 2021 | Pg 5Image: Shikha Awasthi
CARTILAGE REPAIR USING
HIGH-STRENGTH HYDROGELS
Cartilage is a type of connective required mechanical strength and puncture The study, designed by postdoctoral fellow
tissue that acts as a shock absorber resistance. Shikha Awasthi, found that the most stable
and deters abrasion between bones. composite hydrogel (PAM+TiO2+CNT)
Although it is usually tough and flexible, Researchers at the Departments of had remarkable self-healing ability, high
injuries, hormonal abnormalities or Materials Engineering, Mechanical mechanical strength, and compatibility with
diseases can cause damage and make Engineering and Inorganic and Physical biological tissue. Its dense and compact
it hard for the cartilage to heal. Recent Chemistry in IISc have now developed structure helps it withstand degradation.
advances are focused on using polymers hybrid hydrogels by combining PAM with The researchers also used a method called
called hydrogels to replace injured either carbon nanotubes (CNTs) or titanium needle insertion to show that the hybrid
or diseased cartilage. Despite having dioxide (TiO2) or both. They also carried hydrogel is puncture-resistant. Such
some properties needed for cartilage out computational studies to understand materials offer great promise for cartilage
tissue repair, commonly-used hydrogels the binding features and structure of these repair applications.
made of polyacrylamide (PAM) lack the hybrid hydrogels.
- Debraj Manna
Image: Navaneetha Krishnan Ravichandran
IDENTIFYING NEW MATERIALS WITH NOVEL
THERMAL PROPERTIES
In crystalline electrical insulators, heat is New research led by Navaneetha with unusually weak rates of three-
carried by phonons, which are quantised Krishnan Ravichandran at the phonon collisions. In the new study,
vibrations of the crystal lattice. As these Department of Mechanical Engineering the researchers used these insights to
phonons travel through the material, they now provides a way to identify materials predict an unusual pressure-dependence
collide with each other, thereby limiting that show intriguing temperature- and of the k of a material called boron
the material’s thermal conductivity (k). pressure-dependencies of k, without phosphide (BP) ‒ the material showed a
Predicting how frequent and strong these performing these full, expensive sharp rise in k with pressure, with a peak
collisions are (“collision rates”) for each computations. and subsequent drop, in stark contrast to
material under different experimental the linearly increasing trend seen in most
conditions is computationally expensive. In an earlier publication, Ravichandran other materials.
This can slow down the discovery of new and collaborator David Broido at
materials, with their k values and trends Boston College, USA developed a set
tailored to our needs. of guidelines to identify materials - Navaneetha Krishnan Ravichandran
KERNEL | ISSUE 7, 2021 | Pg 6Photo courtesy: Ashwini Ratnoo
EYE IN THE SKY
ASHWINI RATNOO’S RESEARCH IS GEARED TOWARDS MAKING DRONE FLIGHT MORE EFFICIENT FOR
HEALTHCARE, TRANSPORTATION AND OTHER SERVICES
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), popularly it must be programmed with computer the corridor. CORRIDRONE allows for
known as drones, are small aircraft that fly algorithms that make human-like decisions safe point-to-point movement of multiple
without a pilot. Drones can weigh anywhere with precision. Ashwini’s team develops drones without collision and can be set up
from a few grams to over 100 kilograms, algorithms that plan and control the in any given airspace.
depending on their use. They either have a trajectories of UAVs, particularly in
ground-based controller or are completely complex and urban settings. Unmanned vehicles are not restricted to
autonomous, with a built-in controller in the sky. Autonomous ground vehicles,
the form of a computer program that guides Here is an example: It is not easy to considered the future of road travel, are
them. organise timely delivery of medicines or also on Ashwini’s radar. With support from
organs for transplantation in a crowded the Wipro IISc Research and Innovation
UAVs have a wide range of applications city. A lot of manpower is involved, and Network (WIRIN), his team is involved in
including surveillance, cargo transport, elaborate traffic management is needed trajectory planning for such vehicles. “In
warfare, agriculture, journalism and if they are transported by road. This is an autonomous ground vehicles, perception
recreation, to name a few. These vehicles easy job for a drone, but flying one over is slightly more challenging because there
have also been of great help during the a populous urban space comes with many are a lot of occlusions [obstructions] to
COVID-19 pandemic, in remote surveillance safety concerns, explains Ashwini. That is vision. For example, there’s a wall on the
and disinfection of areas. why drones are still not being used to their left, a tree on the right and so on. So, a lot
full capacity and potential. of effort goes into the perception side,”
The controller of an autonomous vehicle says Ashwini. The specific challenges, be
acts as its brain and has two functions: To address this issue, his lab is working it for aerial or ground vehicles, pertain to
perception and planning. It must perceive on developing ‘Drone Skyways’ in the space used by an autonomous vehicle.
its surroundings and execute a suitable plan collaboration with the Robert Bosch The trajectory must be compatible with
on how to move in that situation. Ashwini Centre for Cyber Physical Systems the dynamics of the vehicle. For example,
Ratnoo’s lab at the Department of Aerospace (RBCCPS) and ARTPARK at IISc. They are a path riddled with sharp turns is
Engineering works on the planning part of developing trajectory planning algorithms difficult for the vehicle to manoeuvre if it
this autonomous UAV brain. that create a corridor, a virtual road, encounters an obstacle. Another challenge
for UAVs to travel safely. These drones is the computational complexity of the
Research on drones has been gaining fly at an altitude designated as “Class algorithm itself. A complex algorithm
more prominence these days because G” that is closest to the surface of the takes longer to execute, making the
they can fly beyond the visual line of earth. Flying a drone in this airspace vehicle inefficient.
sight (BVLOS) of the person controlling requires a lot of preparedness in terms
them. They can provide visuals of even of safety and security. Ashwini’s research The algorithms that his team is
the most inaccessible areas making them group has participated in developing developing are based on the theory of
indispensable in disaster management “CORRIDRONE”, a novel drone skyway dynamical systems. “What we use is
and warfare, among other fields. For a framework with an efficient design that something called bifurcation theory,
drone to be able to function autonomously, includes geo-fencing, a virtual fence along which essentially generates a variety of
KERNEL | ISSUE 7, 2021 | Pg 7Indoor motion capture facility for UAVs (Photo courtesy: Autonomous Vehicles Laboratory)
motion patterns for the drones based on task. Work on drone recovery methods from the same department in 2009, Ashwini
the same control structure, but by varying is underway in collaboration with IIT went to Israel for his post-doctoral studies at
just a certain parameter within that Madras. Ashwini’s lab has also worked the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology.
control structure,” explains Ashwini. closely with the Ministry of Defense in the He returned to India in 2012 to join the
past. These projects were funded by DRDO Department of Aerospace Engineering as an
Trajectory plans are also created for the and BrahMos Aerospace, via the Centre for assistant professor.
use of multiple UAVs in the same airspace Excellence in Hypersonics at IISc.
to perform tasks like surveillance. This With his work on drones, Ashwini hopes to
effort is sponsored by the Ministry of Ashwini’s tryst with science began during make remote corners of the country more
Education’s IMPRINT India Initiative. his school days. “[The] more shaping accessible. The applications of drones
element was in high school, where are endless, and no longer limited to
Apart from his work with RBCCPS and we got introduced to mechanics and I surveillance and cargo movement. In the
WIRIN, Ashwini has several other was fascinated by particle mechanics; future, drones will be one of the sought-
collaborative projects. With IIIT Delhi, the how points move in a plane, motion of after modes of transport, according to him.
team is working on landing trajectories bodies, and so on,” he says. To pursue “People are already talking about drone
for drones, also called ‘vertical descent’. his interest in the physical and system taxis.”
With the University of Cincinnati in the sciences, he obtained a Bachelor’s degree
US, they have worked on multi-drone in engineering from MBM Engineering
coordination known as ‘platooning’, College in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, followed by - Sangeetha Devi Kumar
wherein a group of drones follows a Master’s degree from the Department of
a leader drone to perform a specific Aerospace Engineering at IISc. After a PhD
UAV trajectory through multiple obstacles (Image courtesy: Autonomous Vehicles Laboratory)
Office of Communications (OoC) EDITORIAL TEAM DESIGN
Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Deepika S TheFool.in
Karthik Ramaswamy
Bengaluru - 560012
Narmada Khare
kernel.ooc@iisc.ac.in Ranjini Raghunath (Coordinator)
https://kernel.iisc.ac.in/ Samira Agnihotri
KERNEL | ISSUE 7, 2021 | Pg 8You can also read